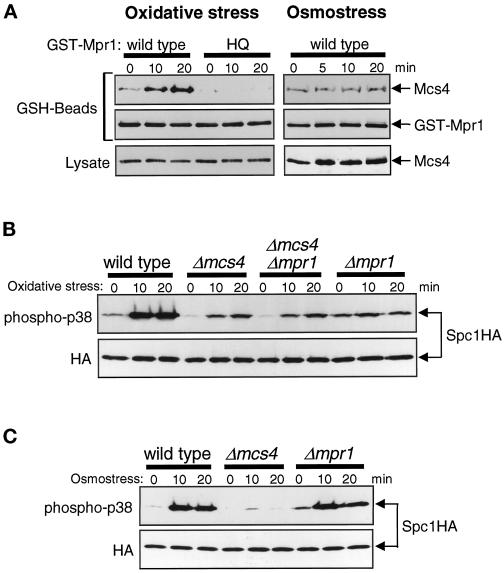
Figure 4.
Mpr1 functions upstream of the Mcs4 response regulator. (A) Oxidative stress induces physical association between Mpr1 and Mcs4. Strain CA337 has chromosomal mcs4+ tagged with the sequence encoding the myc epitope. This strain was transformed with pREP1-KZ-mpr1 and pREP1-KZ-mpr1HQ plasmids, which express GST fusion proteins of wild-type and His-221→Gln mutant Mpr1, respectively, under the regulation of the thiamine-repressible nmt1 promoter. The transformants were grown in EMM2 medium with 0.03 μM thiamine to induce expression of the GST fusion proteins at a low level and treated with either oxidative stress induced by 0.3 mM H2O2 (left panels) or high-osmolarity stress induced by 0.6 M KCl (right panels) for the indicated times. Cell lysates were absorbed to GSH-Sepharose beads, and after extensive washes, proteins bound to the beads (GSH-Beads) were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-myc and anti-GST antibodies. The amount of Mcs4 detected in the crude cell lysates (Lysate) did not change significantly after the stress treatments. (B) Wild-type (KS1376), Δmcs4 (CA220), Δmpr1 (CA279), and Δmcs4 Δmpr1 (CA420) strains carrying the spc1:HA6H allele were grown to midlog phase at 30°C in YES medium and treated with oxidative stress induced by 0.3 mM H2O2. Aliquots of cells were harvested at the indicated times, and Spc1 was purified by Ni-NTA chromatography, followed by immunoblotting with anti-phospho-p38 and anti-HA antibodies. The pattern of Spc1 activation in the Δmcs4 Δmpr1 double mutant is identical to that in the Δmcs4 mutant before and after oxidative stress. (C) Wild-type (KS1376), Δmcs4 (CA220), and Δmpr1 (CA279) strains were treated with high-osmolarity stress induced by 0.6 M KCl, and Spc1 activation was examined as described for B.