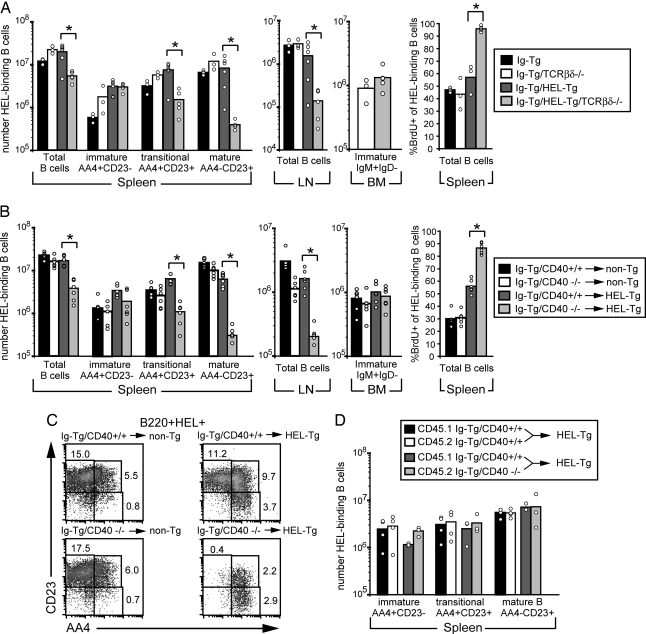
Fig. 1.
Reduced survival of HEL autoantigen-binding B cells in T cell-deficient mice and in mice lacking CD40. (A) Adult mice of the indicated types were given water containing BrdU for 5 days and analyzed. Spleen and lymph node (LN) cells were stained for CD19, HEL, AA4, and CD23 to distinguish immature (AA4+CD23−), transitional (T2- and T3-inclusive and AA4+CD23+), and mature (AA4−CD23+) HEL-binding B cells (8). Bone marrow (BM) cells were stained for B220, IgM, and IgD, and immature B cells were identified as B220+IgM+IgD−. Spleen cells were also stained for B220, HEL binding, and BrdU. Data show three to six mice per group from two separate experiments. (B) Bone marrow from CD40+/+ Ig Tg or CD40−/− Ig Tg mice was used to reconstitute lethally irradiated non-Tg and HEL Tg recipient mice. After 6–8 weeks, mice were given water containing BrdU for 5 days and then analyzed as in A. Data show six mice per group from one set of bone marrow chimeras and are representative of two experiments. (C) Examples of AA4 and CD23 profiles of splenic B cells of mice in B. Cells were stained for B220, HEL binding, CD23, and AA4 and pregated on size, B220, and HEL binding (B220+HEL+). (D) Bone marrow from CD45.1-positive CD40+/+ Ig Tg mice and CD45.2-positive CD40+/+ Ig Tg or CD45.2-positive CD40−/− Ig Tg mice was mixed at a 1:1 ratio and used to reconstitute lethally irradiated HEL Tg recipient mice. After 6–8 weeks, spleen cells were stained for CD45.1, CD19, AA4, CD23, and HEL-binding. Data show three to four mice per group from one set of bone marrow chimeras and are representative of two experiments. ∗, P < 0.002 by Student’s t test.