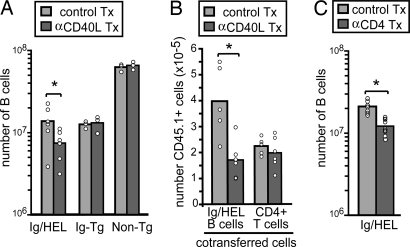
Fig. 2.
CD40L blocking and depletion of CD4 T cells lead to similar reductions in autoantigen-binding B cell numbers. (A) Non-Tg, Ig Tg, and Ig/HEL Tg mice were treated with 250 μg of anti-mouse CD40L (clone MR1) or control IgG on days 0, 2, and 5. After 7 days, HEL binding (in Ig Tg and Ig/HEL Tg mice) or total (in non-Tg mice) B cells in spleen and lymph nodes were enumerated. Ig/HEL Tg data show six mice from two experiments; non-Tg and Ig Tg data show three mice from one experiment. (B) CD45.1-positive Ig/HEL Tg cells were transferred into CD45.2-positive Ig/HEL Tg recipients 1 h after treatment of recipient mice with anti-CD40L or control antibody. Mice were treated and analyzed as in A by using anti-CD45.1 to identify the transferred cells. Data show five to six mice from two experiments. (C) Depletion of CD4+ T cells leads to decreased survival of autoreactive B cells. Ig/HEL Tg mice were treated with 1 mg of anti-mouse CD4 (clone GK1.5) (d0, d4) to deplete CD4 T cells. After 9 days, HEL-binding B cells were enumerated as in A and B. Data show nine mice from three separate experiments. Tx, antibody-treated. ∗, P < 0.05 by Student’s t test.