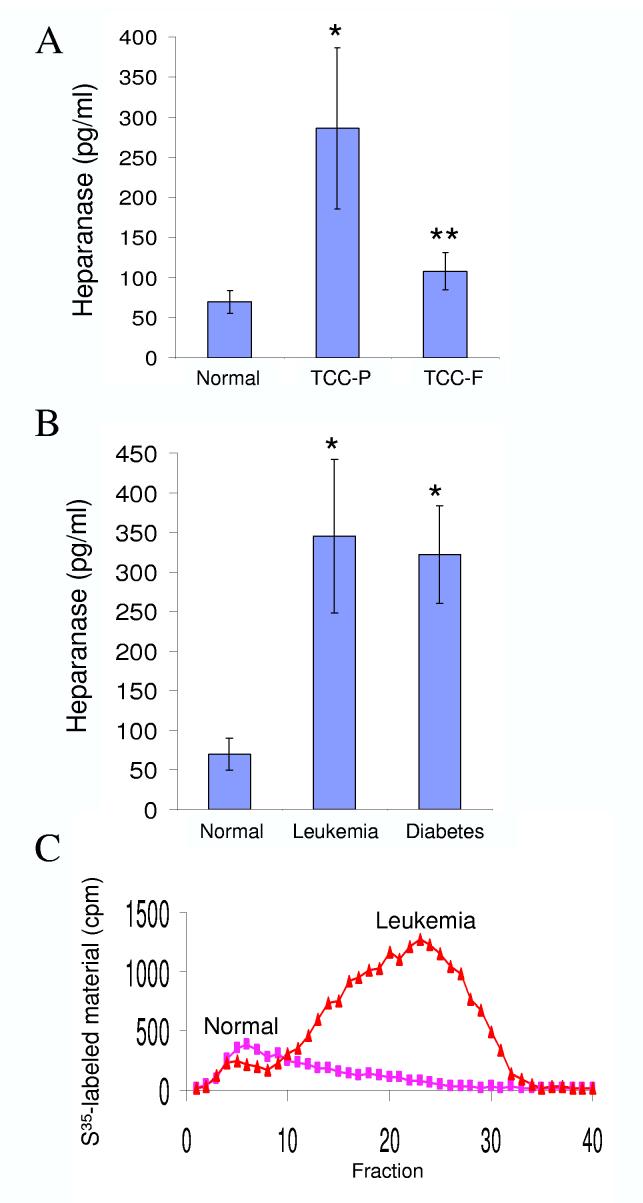
Figure 3.
Detection and quantification of heparanase in urine samples. A. ELISA. Urine samples were collected from normal human volunteers (n=27) and from transitional bladder cell carcinoma prior to (A, TCC-P, n=10), and following surgical resection of the primary tumor (A, TCC-F, n=19). Urine samples were also collected from leukemia (B, n = 8: 4 AML, 2 ALL, 2 CLL) and diabetic (n = 34) patients with kidney complications. Heparanase levels were determined in duplicates by the ELISA method and the results are expressed as mean + SE. It should be noted that heparanase levels in the urine of healthy donors was often below the assay sensitivity, and the exact amounts above baseline could not be determined. Actual heparanase levels in the urine of healthy donors may be, thus, lower than those calculated here. C. Enzymatic activity. Urine collected from representative healthy volunteer and leukemia patient was incubated (18 h, 37°C, pH 6.0) with sulfate-labeled ECM and heparanase activity was determined as described in “Materials and Methods”.