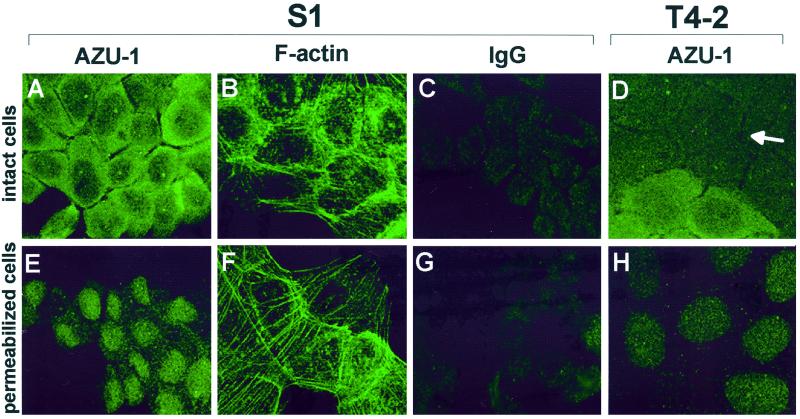
Figure 4.
AZU-1 is a predominantly cytoplasmic protein in S1 and T4-2 cells. After 4 d in culture, cell monolayers were either directly fixed with 2% paraformaldehyde (A–D) or permeabilized with Triton X-100 before fixation (E and F). Cells were immunostained with affinity-purified anti-AZU-1 polyclonal antibody (A, D, E, and H) or with an equivalent amount of purified rabbit IgG (B and F). Primary antibodies were detected using an FITC-conjugated secondary antibody. F-actin was visualized in S1 cells using FITC-phalloidin. Confocal images in A, C–E, G, and H show a 0.4-μm optical section through the center of the cell nuclei. In both S1 and T4-2 cells, AZU-1 is found primarily in the cell cytoplasm, albeit at generally lower levels in the T4-2 cells (see arrow in D for typical T4-2 expression pattern). In both cells, the cytoplasmic pool of AZU-1 is detergent extractable, indicating that AZU-1 is not likely to be tightly associated with the insoluble cytoskeleton. (F-actin was monitored as a positive indicator of detergent resistance.) A minor, detergent-resistant pool of AZU-1 is found throughout nuclei in dim speckles as well as in distinct subnuclear foci. All images were recorded at 120× magnification.