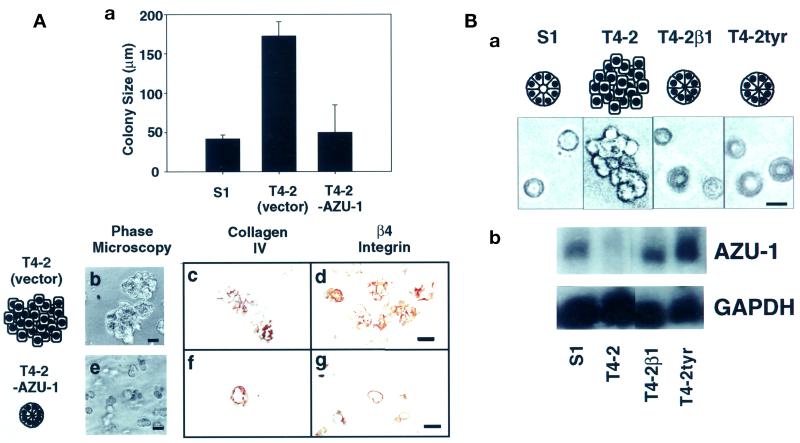
Figure 6.
Increased AZU-1 expression levels correlate with phenotypic reversion in 3D rBM assays. (A) AZU-1 induces phenotypic reversion. S1, T4-2 (vector-infected), and T4-2-AZU-1 cells were embedded as single cells in 3D rBM assays. After 10 d in culture, the colonies were measured (expressed as colony diameter in micrometers ± SE) and imaged using phase microscopy (a, b, and e). Cultures were immunostained with antibodies specific for collagen IV (c and f) or β4 integrin (d and g). (B) AZU-1 is reexpressed upon EGFR- and β1 integrin-induced phenotypic reversion. (a) S1 and T4-2 cells were cultured in 3D rBM assays in the absence or presence of functional inhibitors of β1 integrin (T4-2β1) or EGFR (T4-2tyr; tyr, tyrphostin). Unlike control cells, inhibitor-treated T4-2 cells exhibit an S1-like, acinar phenotype in 3D cultures. (b) Total RNA harvested from these cultures was analyzed in Northern blots using an AZU-1-specific probe. GAPDH was used as a loading control. AZU-1 expression is restored to S1-like levels in T4-2 cells that have undergone phenotypic reversion in the 3D rBM assay. Bars, 50 μm.