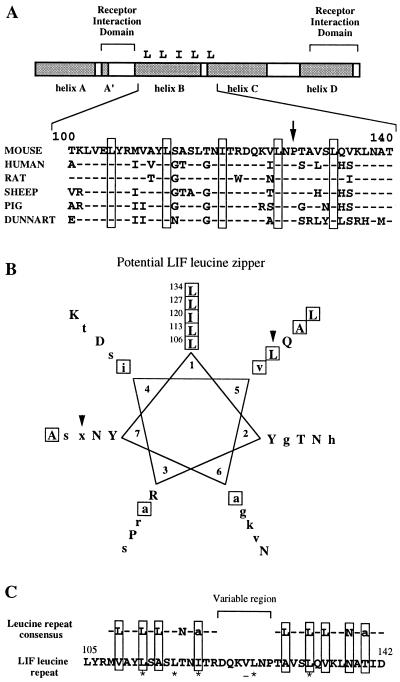
Figure 6.
Conserved protein motifs in the LIF sequence. (A) Schematic diagram of the LIF protein showing the position of the conserved leucine zipper-like structure relative to the receptor interaction domains in five eutherian mammals and one marsupial. Dashes indicate residues conserved with the mLIF gene. Boxes indicate conserved leucine residues. A conserved proline residue is marked by the arrow. Helices in the LIF secondary structure (Robinson et al., 1994) are shaded. Numbers indicate corresponding residues in the mLIF sequence described by Gearing et al. (1987). (B) Potential LIF leucine zipper represented as a wheel diagram. Residues conserved in at least five of the six LIF sequences are capitalized; lowercase residues are conserved in at least three of the six LIF sequences; x indicates a nonconserved residue; and hydrophobic residues are boxed. Arrowheads indicate nonheptad residues that were mutated in this analysis. (C) Alignment of the mLIF leucine motif with the consensus sequence for a leucine-rich repeat. Asterisks indicate residues required for iLIF activity as determined by mutation. The valine residue that is nonessential for iLIF activity is underlined.