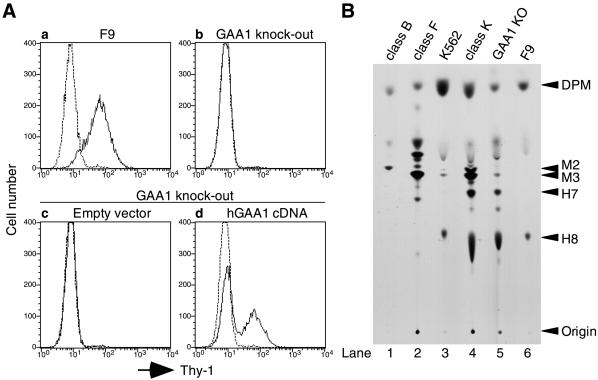
Figure 2.
Characterization of GAA1-knockout cells. (A) Surface expression of GPI-anchored proteins. Parent F9 cells (a) and GAA1-knockout cells (b) were analyzed for the surface expression of Thy-1. GAA1-knockout cells transiently transfected with an empty vector (c) or human GAA1 cDNA (d) were stained for Thy-1 2 d after transfection. Solid and dotted lines indicate staining with anti–Thy-1 antibody and that with secondary reagent alone, respectively. (B) Biosynthesis of GPI anchor intermediates analyzed by TLC. Cells were metabolically labeled with [3H]mannose for 45 min in the presence of tunicamycin, and mannolipids were analyzed by TLC and fluorography. Identities of spots and origin are indicated on the right. DPM, dolichol–phosphate-mannose; M2 and M3, GPI intermediates bearing two and three mannose residues, respectively; H7 and H8, mature forms of GPI. Lanes 1 and 2, class B and F GPI-deficient mutants used to help identify the spots; lanes 3 and 4, wild-type and class K mutant of K562 cells; lanes 5 and 6, GAA1-knockout and wild-type F9 cells.