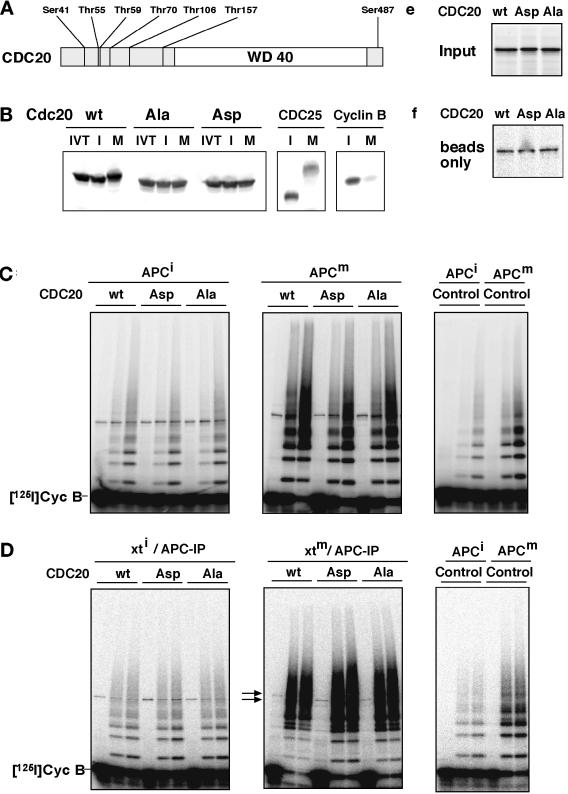
Figure 7.
Analysis of CDC20 phosphorylation mutants. (A) Schematic representation of the amino acid sequence of CDC20 and of the threonine and serine residues that were mutated to either alanine (CDC20Ala) or aspartate (CDC20Asp) residues is shown. The position of the WD40 repeat domain is indicated. (B) 35S-labeled in vitro translation products (IVT) of wild-type CDC20 (wt), CDC20Ala (Ala), and CDC20Asp (Asp) were incubated in Xenopus interphase (I) or mitotic (M) extracts and subsequently analyzed by SDS-PAGE and phosphorimaging. To control the interphase and mitotic state of the extracts, 35S-labeled CDC25 and cyclin B were added and analyzed side by side. (C) Immunopurified Xenopus interphase APC (APCi) or mitotic APC (APCm) were incubated with 35S-labeled proteins as described in b or with an in vitro translation mixture without DNA (Control), washed stringently, and subsequently analyzed for cyclin B ubiquitination activity. Samples from the ubiquitination assay were taken at 0, 15, and 30 min. (D) In vitro–translated proteins as in b were incubated in Xenopus interphase (xti) and mitotic (xtm) extracts for 30 min before APC was immunoprecipitated from these extracts, washed, and analyzed for ubiquitination activity. (E) One-eightieth of the amount of 35S-labeled proteins used in C and D is shown. (F) The amount of 35S-labeled proteins that bind nonspecifically to the antibody-coupled beads is shown. IP, immunoprecipitate. [125I]Cyc B, 125I-labeled recombinant cyclin B fragment 13–110.