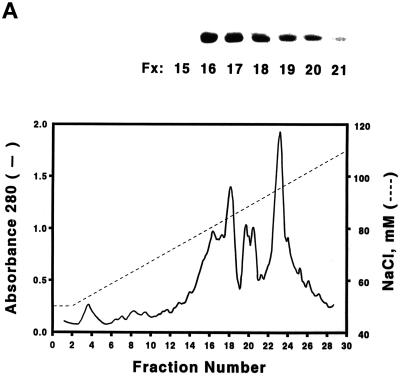
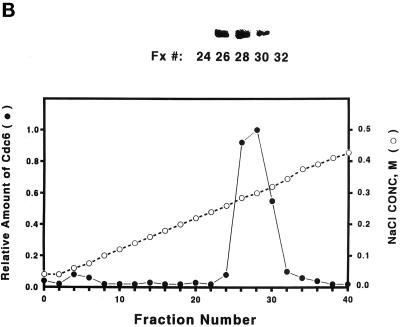
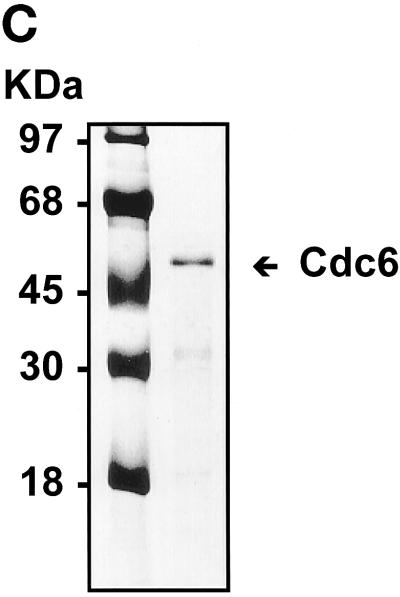
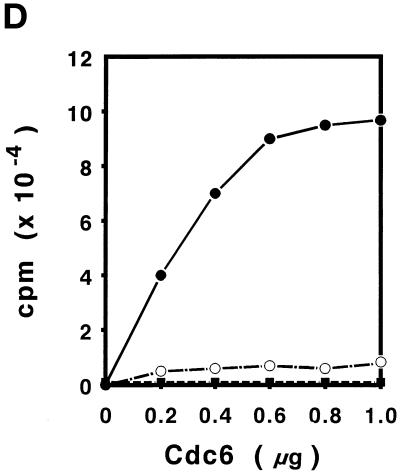
Figure 1.
Purification of S. cerevisiae Cdc6. (A) Yeast extracts were passed through a DE-52 column and reloaded onto a FPLC Mono-Q 16/10 column. The location of Cdc6 was determined by protein blotting (top). The profile of Mono-Q chromatography is shown. Plotted is the relative position of Cdc6 (top), protein concentration (OD280), and NaCl concentration (mM) by FPLC fraction number. (B) dsDNA affinity column chromatography. The elution of Cdc6 was monitored by protein blotting (top). Plotted is the relative position of Cdc6 (●) and NaCl concentration (M, ○) by FPLC fraction number. (C) SDS-PAGE analysis of purification. (Lane 1) Prestained protein molecular mass standards from Life Technologies/BRL. Numbers correspond to the molecular masses of standard proteins. (Lane 2) Five nanograms of the purified yeast Cdc6 protein. Proteins were fractionated with the use of PhastGel SDS-PAGE (Pharmacia). The gel was silver stained. (D) The binding of purified yeast Cdc6 protein to DNA. The nitrocellulose DNA-binding assay was performed as described in MATERIALS AND METHODS. The effect of increasing concentrations of yeast Cdc6 protein on dsDNA (●) and ssDNA (○) is shown. Reaction without Cdc6 is also indicated (▪).