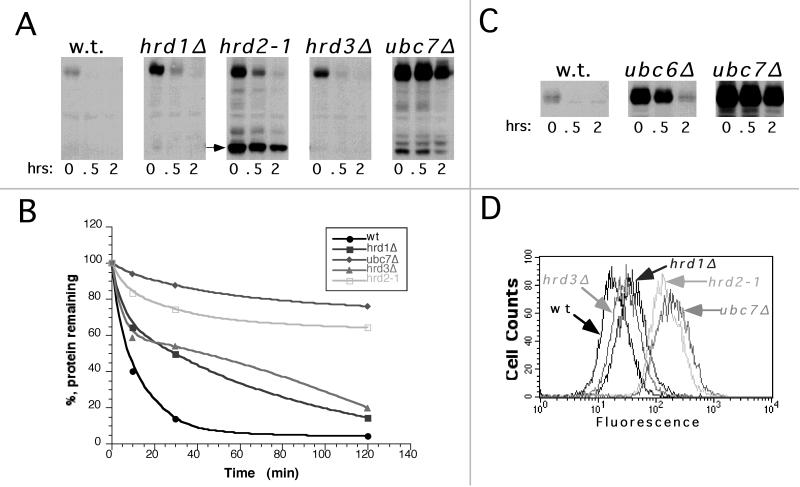
Figure 2.
Deg1-Hmg2p was completely dependent on UBC7 but only partially dependent on HRD1, HRD3, and UBC6. (A) Cycloheximide–chase assay of strains expressing Deg1-Hmg2p in a wild-type (RHY1610), hrd1Δ (RHY1613), hrd2-1 (RHY1615), hrd3Δ (RHY1617), and ubc7Δ (RHY1619) genetic background. After addition of cycloheximide, lysates were prepared at the indicated times and immunoblotted with the 9E10 anti-myc antibody. An arrow marks the 60-kDa proteolytic fragment seen in hrd2-1 strains. (B) Pulse–chase analysis of the identical strains in A. Cells were pulse-labeled with 35S-Express for 10 min and chased for the indicated times. Deg1-Hmg2p was immunoprecipitated and analyzed by SDS-PAGE and autoradiography. The levels of Deg1-Hmg2p for each time point were determined by densitometric analysis of the autoradiograms. (C) Cycloheximide–chase assay of strains expressing Deg1-Hmg2p in a wild-type (RHY1610), ubc6Δ (RHY1656), and ubc7Δ (RHY1619) genetic background. (D) Fluorescence histogram of strains expressing Deg1-Hmg2p–GFP in a wild-type (RHY1374), hrd1Δ (RHY1575), hrd2-1 (RHY1577), hrd3Δ (RHY1579), and ubc7Δ (RHY1581) genetic background. Strains were analyzed directly from early log-phase cultures. Each histogram represents 10,000 cells.