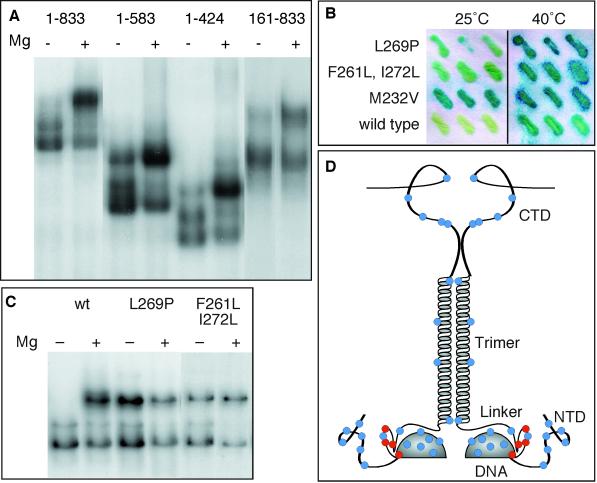
Figure 6.
Mapping the regions on which the O2− response depends. (A) DNA-binding reactions using whole-cell extracts from cells expressing the indicated HSF derivatives were treated with 10 mM MgCl2 to stimulate O2− production and to induce formation of complex III. (B) β-Galactosidase assays of yeast carrying HSFL269P, HSFF261L,I272L, HSFM232V, or wild-type HSF are shown. Cells were grown in triplicate at 25°C with or without a 2-h heat shock at 40°C and then analyzed by a β-galactosidase filter-lift assay. (C) DNA-binding reactions using whole-cell extracts from cells expressing wild-type HSF (wt), HSFL269P, or HSFF261L,I272L are shown. (D) A schematic summary of mutations that do (red dots) or do not (blue dots) affect complex III formation is shown. Mutations in the N-terminal domain (NTD) were T43C, S69C, S89C, S111C, A128C, and S151C. Mutations in the DNA-binding domain (DNA) were S181C, T189C, E196C, E208C, S221C, M232V, and Q247C. Mutations in the flexible loop between the DNA-binding domain and the flexible linker were L269P and K271C and the double mutant F261L, I272L. A mutation in the linker (Linker) was S295C. Mutations in the trimerization domain (Trimer) were I347C, M381C, Y356C, and L400C. Mutations in the C-terminal domain (CTD) were A543C, S548C, S568C, S626C, S655C, and S788C.