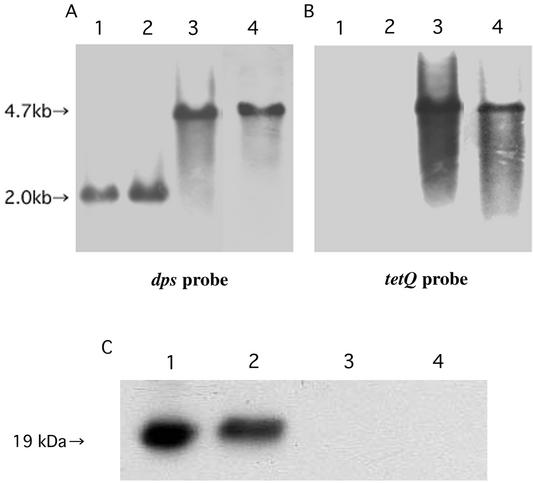
FIG. 4.
Proof of authenticity of the P. gingivalis dps mutant KDP141 and the ftn dps double mutant KDP142. (A and B) Southern blot analyses of the chromosomal DNA. The chromosomal DNAs of the wild-type ATCC 33277 (lane 1) and the ftn mutants KDP139 (lane 2), KDP141 (lane 3), and KDP142 (lane 4) were digested with NcoI. The resulting DNA fragments were subjected to agarose gel electrophresis, followed by blotting. Hybridization was performed by using the 0.6-kb NdeI-BglII fragment of pKD390 as a dps probe (A) and the 2.7-kb BamHI-BglII fragment of pKD375 as a tetQprobe (B). (C) Immunoblot analysis. After purified P. gingivalis Dps (lane 1) and the cell extracts of ATCC 33277 (lane 2), KDP141 (lane 3), and KDP142 (lane 4) were electrophoresed through an SDS-polyacrylamide gel, the proteins were transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane and immunoreacted with antiserum against P. gingivalis Dps.