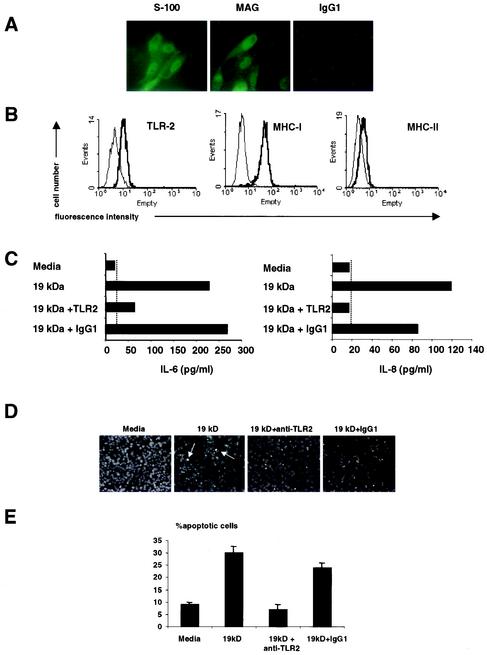
FIG.1.
Expression of TLR2 and TLR2-induced apoptosis in a human Schwann cell line. (A) The human Schwann cell line expressed S-100 and MAG, markers compatible with Schwann cells. (B) Schwann cells were labeled with anti-TLR2, anti-MHC-I, and anti-MHC-II MAbs (thick lines) or isotype control antibodies (thin line), followed by phycoerythrin- or FITC-conjugated goat anti-mouse antibodies, and examined by flow cytometry. The results shown are representative of three independent experiments that gave similar results. (C) Schwann cells produced IL-6 and IL-8 in response to the 19-kDa lipopeptide. The ability of Schwann cells to release IL-6 and IL-8 in response to the 19-kDa lipopeptide was dependent on TLR2. Broken lines indicate the minimum level of detection of the cytokine ELISA. (D) The 19-kDa lipopeptide induced apoptosis in Schwann cells in a TLR2-dependent manner. Arrows indicate apoptotic cells. (E) Quantification of apoptotic cells. The nuclear morphology of apoptotic cells was assessed after Hoechst staining and exposure to UV light. The results from one representative experiment of three are shown. For quantitative analysis, percent nuclear fragmentation was calculated based on an examination of at least 500 target cells in multiple vision fields. The data are shown as mean and standard deviation.