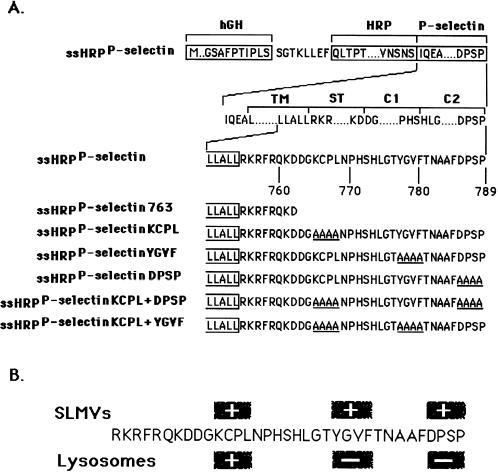
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of HRP-P-selectin chimeras and localization of major targeting determinants within the cytoplasmic tail of P-selectin. (A) The top line shows the position of components used for construction: hGH, human growth hormone signal sequence; P-selectin, transmembrane and cytoplasmic domain of P-selectin. The cytoplasmic domain of P-selectin was divided into the stop transfer (ST), C1, and C2 subdomains according to exon–intron boundaries (Johnston et al., 1989). The bottom part shows the full amino acid sequences of the cytoplasmic domains of the chimeras. The carboxyl-terminal end of the transmembrane domain shown is boxed. The amino acids substituted for alanine are shown to the left of the diagram and included in name of the chimera. ssHRPP-selectin763 is a chimera in which both the C1 and C2 subdomains are removed. (B) Localization of SLMV and lysosomal targeting signals within the cytoplasmic domain of P-selectin. The determinants inactivation of which reduces targeting to the level of tailless ssHRPP-selectin763, are shown within the + boxes. The determinants inactivation of which increases targeting over the level of wild-type ssHRPP-selectin, are shown within the − boxes.