Figure 2.
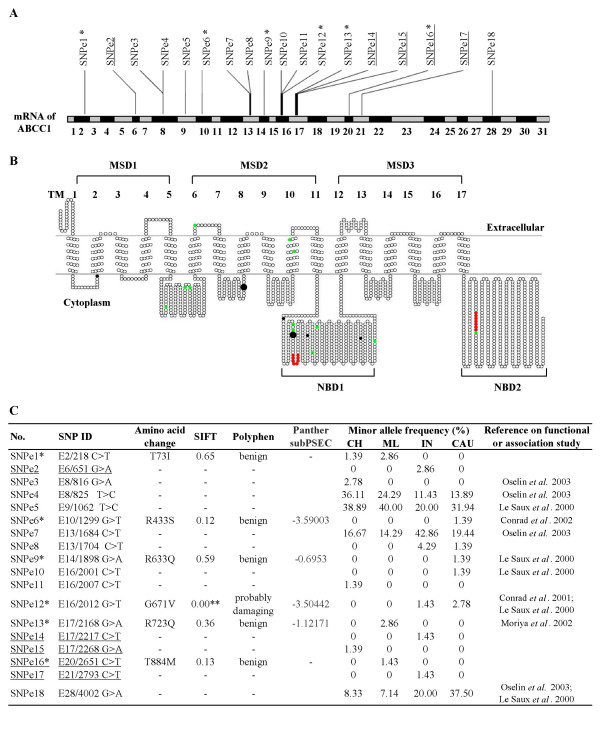
Profiles of the 18 exonic SNPs in MRP1. (A) The distribution of all the exonic SNPs on the mRNA of MRP1 is presented. (B) The topological model of MRP1 protein secondary structure is predicted using the SOSUI program and the positions of the SNPs on the topological image are displayed using the TOPO2 program. Approximate locations of predicted individual transmembrane helices, membrane spanning domains and nucleotide binding domains are indicated as TM 1-17, MSD 1-3 and NBD1-2, respectively. The six nonsynonymous SNPs are highlighted in black while the 12 synonymous SNPs are colored green. Consensus sequences for Walker A and B are highlighted in red. The two nonsynonymous SNPs predicted by PANTHER to be potentially deleterious are highlighted by large black dots. (C) Table showing in silico prediction of functional significance of exonic SNPs and their frequencies in the different populations. SNPs that have previously been utilized for association/functional studies are also presented. For PANTHER prediction, if the subPSEC score is lower than -3.5, it can be interpreted that the amino acid change could have high probability of deleterious functional effect. Note: Underlined SNPs represent SNPs that have not been previously reported. * The six nonsynonymous SNPs are highlighted with single asterisks. ** This SNP is predicted to have effect on the function of the protein.
