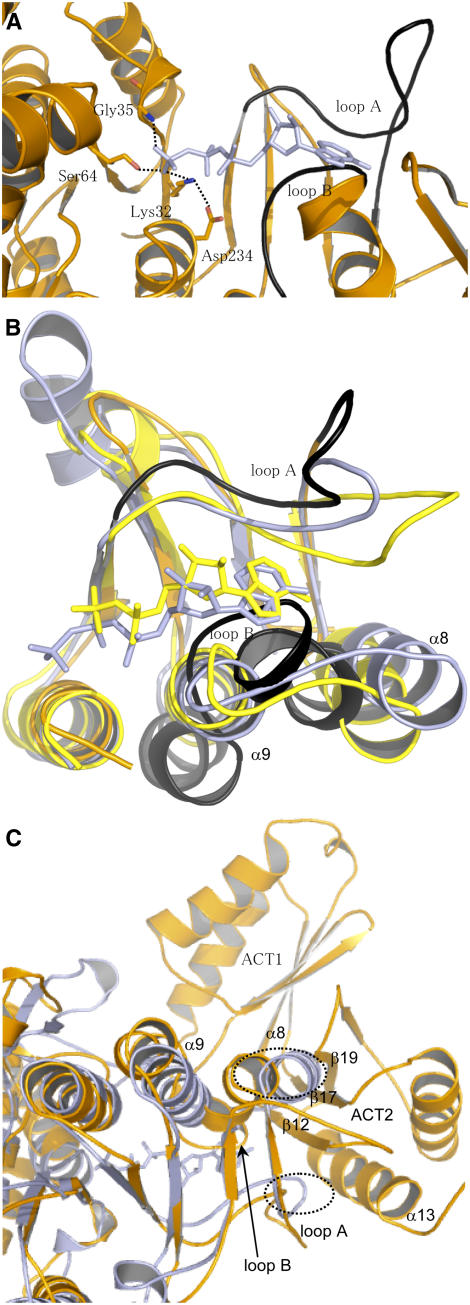
Figure 6.
ATP Binding Site of AK1.
(A) Position of AMP-PNP upon superimposition of the ATP binding sites of NAGK and AK1. The figure shows that (1) Lys-32, Gly-35, and Ser-64 of AK1 have a position suitable for interaction with the β- and γ-phosphate of AMP-PNP, (2) Asp-234 interacts with Lys-32 as observed in the structure of NAGK, and (3) the position of loops A (254 to 273) and B (289 to 296) (in black) of AK1 are incompatible for interaction with the adenosine moiety of AMP-PNP. AMP-PNP is depicted in light blue, whereas AK1 is colored in orange.
(B) Superimposition of the C-terminal lobe of NAGK cocrystallized with AMP-PNP (light blue), CBMK cocrystallized with ADP (yellow), and AK1 (orange). The figure shows that the three structures superimpose very well, except loops A and B of AK1 (in black). Loop B of AK1 makes a steric clash with the nucleotide of NAGK and CBMK. Loop A of AK1 is too distant to interact with the adenosine moiety of AMP-PNP or ADP. (In particular, Asp-254/Asp-262 and Leu-259 cannot interact with the ribose and the adenine moiety of AMP-PNP of NAGK.)
(C) Superimposition of the structure of NAGK (light blue) with the whole monomer of AK1 (orange). Loop A, loop B, helix α8, helix α9, β12, β17, and β19 are indicated. The figure shows that the loops of NAGK corresponding to loops B and A of AK1 make a steric clash (shown in the dashed ovals) with helix α13 and strands β12, β17, and β19 of ACT2 of AK1.