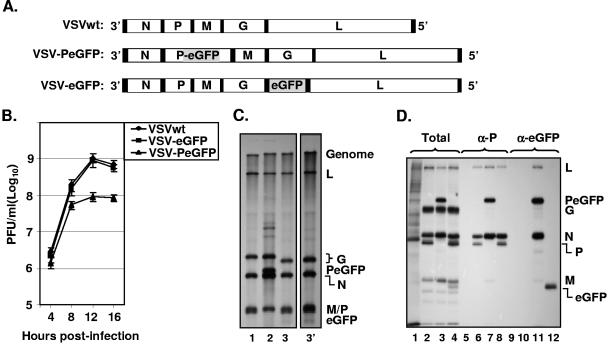
FIG. 2.
Recovery and characterization of recombinant VSV encoding PeGFP fusion protein. (A) Recombinant VSV genome plasmids. VSVwt, the wt VSV genome with the N, P, M, G, and L genes, shown in rectangular boxes; VSV-PeGFP, the VSV genome containing the PeGFP gene in place of the wt P gene; VSV-eGFP, the VSV genome containing the eGFP gene as an extra cistron. Intergenic regions as well as 3′ leader gene and 5′ trailer sequences are shown in black boxes; the eGFP coding region is shaded. (B) Single-cycle growth kinetics of mutant viruses. BHK-21 cells were infected with plaque-purified stocks of wt (VSVwt) or mutant (VSV-eGFP and VSV-PeGFP) viruses at an MOI of 20, and culture supernatants were collected at the indicated time points. The viruses in the supernatants were quantitated by plaque assay. The average values from four experiments are presented, with error bars representing standard deviations. (C) Analysis of VSV mRNAs in cells infected with the mutant viruses. BHK-21 cells were infected with VSVwt (lane 1), VSV-PeGFP (lane 2), and VSV-eGFP (lane 3) at an MOI of 10. Viral RNAs were radiolabeled, analyzed by electrophoresis, and detected by fluorography as described in Materials and Methods. Positions of the VSV mRNAs and full-length genome are indicated at the right. Lane 3′ shows a longer exposure of the autoradiogram to clearly identify the eGFP mRNA that is not readily visible in lane 3. (D) Analysis of proteins in cells infected with recombinant VSVs. BHK-21 cells were infected with VSVwt (lanes 2, 6, and 10), VSV-PeGFP (lanes 3, 7, and 11), and VSV-eGFP (lanes 4, 8, and 12) at an MOI of 10 or left uninfected (lanes 1, 5, and 9). The viral proteins were radiolabeled for 1 h at 4 hpi, analyzed by SDS-PAGE as total (lanes 1 to 4) or immunoprecipitated with anti-P (α-P) (lanes 5 to 8) or anti-eGFP (α-eGFP) (lanes 9 to 12) antibody, and detected by fluorography. The proteins are identified on the right.