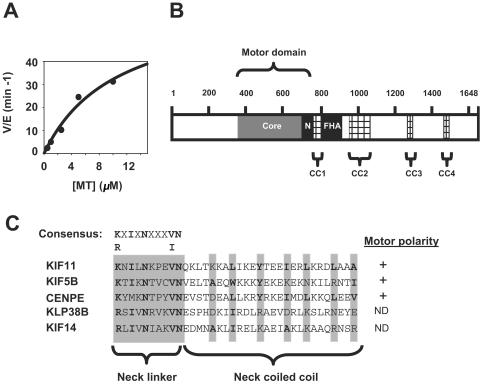
FIG. 1.
KIF14 contains an internal motor domain with plus-end-directed determinants and microtubule-dependent ATPase activity. (A) The ATPase activity of a fragment corresponding to the KIF14 motor domain was assayed as described in Materials and Methods. The ATPase activity of the KIF14 motor (rate [V] per enzyme [E])/min is graphed as a function of microtubule (MT) concentration. (B) The polypeptide chain of KIF14 contains several distinct domains that are likely to be involved in regulating aspects of KIF14 function in vivo. The internal motor domain contains the highly conserved catalytic core (shown in dark gray) and the N-type conserved neck region (N). In addition to the coiled-coil region predicted to exist within the neck, KIF14 contains four additional regions predicted to form coiled-coil regions, CC1 to CC4 (hatched lines). The KIF14 forkhead-associated domain is bordered by CC1 and CC2. (C) The KIF14 neck linker contains the consensus N-type motor sequence K/RXIXNXXXV/IN found in other N-type kinesins (KIF11, KIF5B, and CENPE). In addition, KIF14 contains the N-type neck coiled-coil sequence φ-XX(X)-φ-XXX-φ-XX-φ, where φ denotes a highly conserved hydrophobic residue (shaded in gray and shown in bold type). The plus-end-directed classifications of both KIF14 and KLP38B are putative and have not been biochemically confirmed. +, positive motor polarity; ND, not determined.