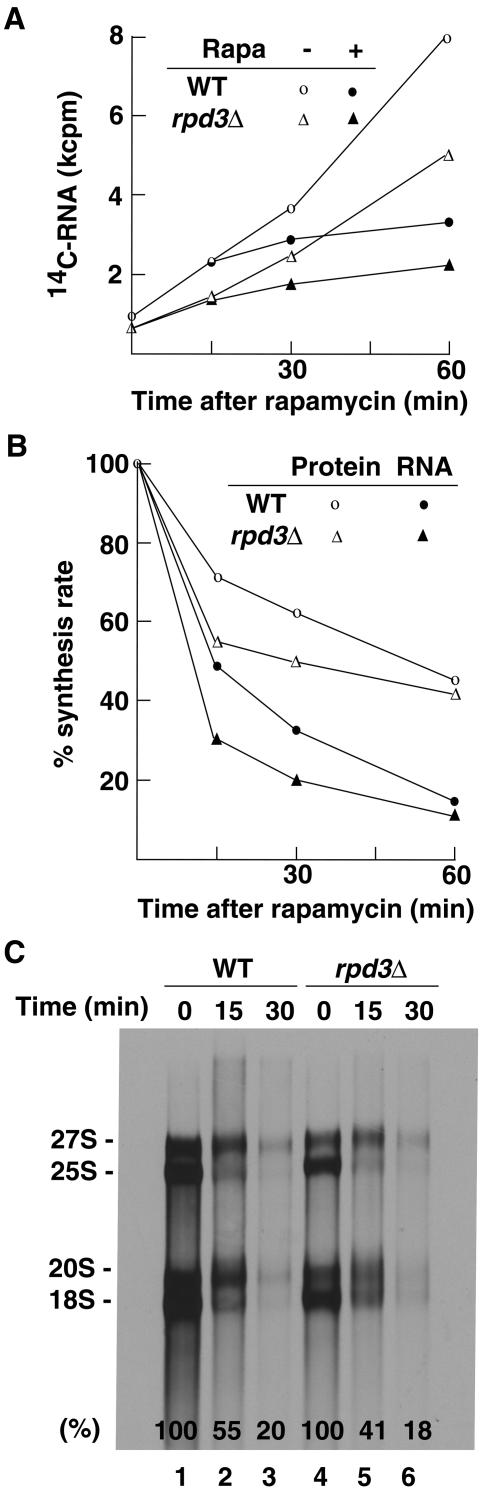
FIG. 4.
Pol I transcription in rpd3Δ mutant cells is as sensitive to rapamycin as Pol I transcription in control WT cells is. (A) Accumulation of total RNA. Both rpd3Δ cells (NOY2015) and control RPD3 (NOY388; WT) cells were grown in SD complete medium supplemented with uracil (5 μg/ml). Each culture was diluted to a cell density of A600 of ∼0.2 and divided into two. [14C]uracil (0.5 μCi/ml) was added, and 15 min later, rapamycin (Rapa) (0.2 μg/ml) or vehicle was added to one of the duplicate cultures, respectively (time zero). Aliquots of the cultures were taken at the indicated times, and the amounts of 14C label (counts per minute in thousands [kcpm]) incorporated into the trichloroacetic acid (TCA)-insoluble fraction (total RNA) were determined. The degrees of inhibition of accumulation between 0 and 30 min and between 30 and 60 min by rapamycin were 64% and 85%, respectively, for the WT, and 58% and 85%, respectively, for the rpd3Δ strains. (B) The rpd3Δ and WT strains were grown in SD complete medium without methionine and were treated with rapamycin (0.2 μg/ml; time zero). Aliquots were taken at indicated times, mixed with [methyl-3H]methionine, and incubated for 5 min. Incorporation of 3H label into the TCA-insoluble fraction (“Protein”; mostly protein together with small amounts of RNA) and the RNA fraction (obtained after phenol extraction) was measured. The values normalized for those at the time of rapamycin addition are shown. (C) In a separate experiment carried out as described above for panel B, RNA samples were prepared after 5 min of 3H pulse-labeling at 15 and 30 min after rapamycin addition, and portions derived from an equal volume of the original culture were subjected to polyacrylamide/agarose composite gel electrophoresis followed by autoradiography. The amounts of 3H in radioactive rRNA bands (precursor 27S and 20S and mature 25S and 18S) were quantified, and the sum of these values normalized for those at time zero were calculated and are indicated near the bottom of each lane.