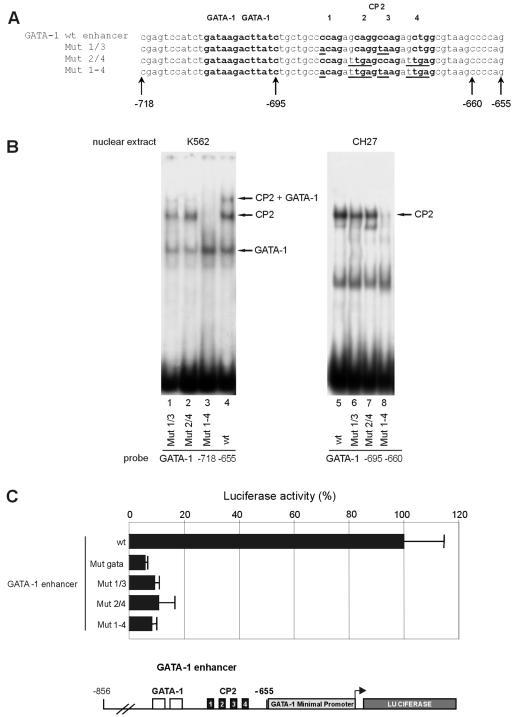
FIG. 3.
CP2 sites on the GATA-1 HS2 enhancer substantially contribute to the transcriptional activity of the GATA-1 gene. (A) Schematic of the wild-type (wt) and mutated GATA-1 HS2 enhancer constructs. The GATA-1 and CP2 consensus sites are boldface, and the mutated bases in the CP2 consensus sites are underlined. (B) The effect of mutations on protein binding. EMSAs with the wild-type and mutated oligonucleotides were performed with extracts from K562 (erythroid) or CH27 (nonerythroid) cells. The positions of the GATA-1, CP2, and GATA-1-plus-CP2 complexes are indicated. The most extensive mutation (Mut 1-4) totally abolished CP2 binding (lanes 3 and 8), but mutations in the single CP2 boxes (Mut 1/3 and Mut 2/4) still allowed significant CP2 binding on the intact CP2 site (lanes 1, 2, 6, and 7). The CH27 nuclear extracts contain CP2 but not GATA-1. (C) Functional luciferase reporter assays with K562 cells of mutants shown in panel A and an additional construct carrying a mutation of the GATA-1 binding site. All three CP2 mutations greatly reduced the ability of the HS2 enhancer linked to the GATA-1 minimal promoter to drive the luciferase reporter, shown schematically in the lower panel.