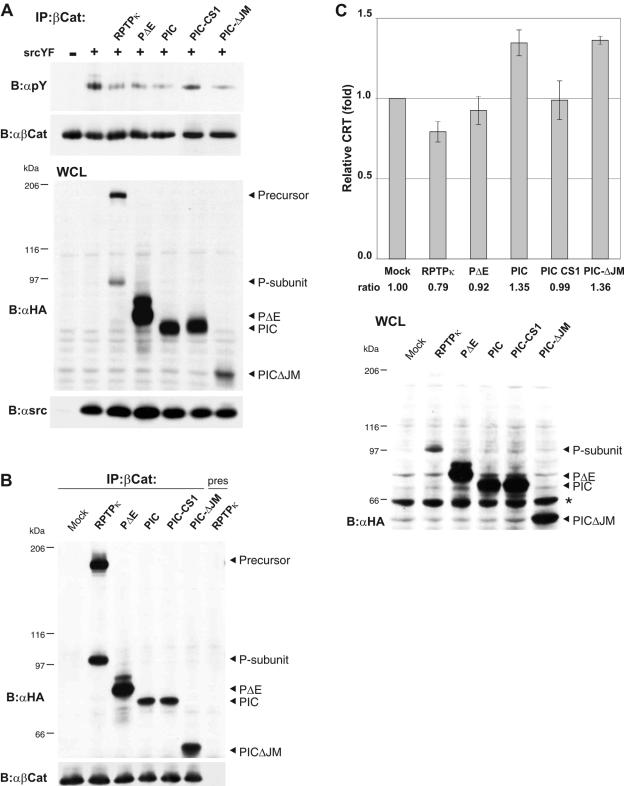
FIG. 7.
PIC is an active protein tyrosine phosphatase that promotes β-catenin-mediated transcription. (A) Dephosphorylation of β-catenin by PIC. HEK293 cells were transfected with empty vector (−) or constitutive active Src (SrcYF) (+) to induce tyrosine phosphorylation of β-catenin. All RPTPκ constructs used here are HA tagged at the C terminus. RPTPκ, PΔE, PIC, PIC-CS1, and PICΔJM were cotransfected, and tyrosine phosphorylation of β-catenin was analyzed (upper panel). Transfection controls are shown below. PIC-CS1 is a catalytically inactive version; PICΔJM is devoid of the juxtamembrane sequence. (B) Coprecipitation of PIC and PICΔJM with β-catenin. HEK293 cells were transfected with either empty vector (mock) or the indicated HA-tagged constructs, and β-catenin was immunoprecipitated. Preserum was used as a control (right lane). RPTPκ-derived constructs were detected with anti-HA antibody. (C) PIC enhances transcriptional activation of β-catenin, whereas RPTPκ suppresses it. HCT116 cells were cotransfected with β-catenin/TCF reporter constructs and either respective RPTPκ plasmids or empty vector (Mock). PIC-CS1 is a catalytically inactive PIC version that harbors a cysteine-to-alanine transition in the proximal PTP domain. Luciferase activity was determined using the dual luciferase kit (Promega), and the data were normalized to the cotransfected cytomegalovirus Renilla plasmid. Error bars represent the standard deviations of triplicate assays. The expression of the RPTPκ constructs is shown in the lower panel (an unspecific bovine serum albumin signal is marked by an asterisk). Abbreviations: α, anti; B, blotting; IP, immunoprecipitation.