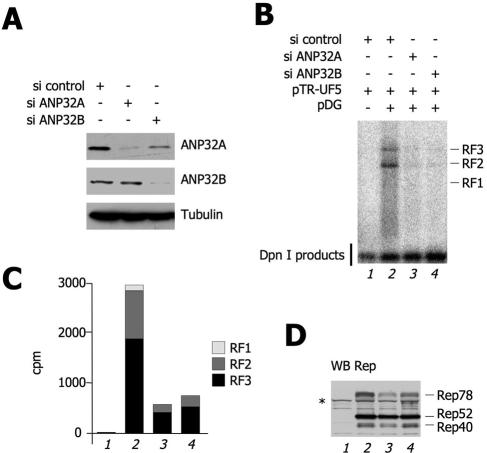
FIG. 5.
ANP32B and ANP32A are required for AAV-2 replication. (A) siRNA-induced knockdown of ANP32A and ANP32B. HEK293 cells were transfected with the indicated siRNA oligonucleotides. Forty-eight hours posttransfection, the endogenous levels of the ANP32A and ANP32B proteins were measured by Western blotting as indicated. A Western blot assay against tubulin is shown as a control. (B) Effect of ANP32A and ANP32B knockdown on AAV-2 DNA replication. HEK293 cells were pretreated either with control, anti-ANP32A, or anti-ANP32B siRNA, as indicated. Thirty-six hours after siRNA transfection, cells were cotransfected with various combinations of plasmids as indicated. Seventy-two hours posttransfection, low-molecular-weight DNA was extracted by the Hirt method and digested with DpnI to remove input bacterial plasmids. An AAV-2 DNA fragment was used in a Southern blot assay to visualize de novo rAAV-2 replication monomer, dimer, and tetramer intermediates, designated RF1, RF2, and RF3, respectively. The lowest band is a DpnI digestion product and serves as an internal transfection and loading control. The same experiment was repeated three times with similar results. (C) Quantification of the AAV-2 replicative forms of panel B. The intensities of the bands corresponding to RF1, RF2, and RF3 were quantified by PhosphorImager and plotted in the histogram as indicated. (D) Levels of expression of the Rep isoforms. Cell extracts from the experiment shown in panel A were analyzed by Western blotting (WB) with an anti-Rep antibody. The asterisk opposite Rep78 indicates an unspecific band also present in the sample not transfected with pDG.