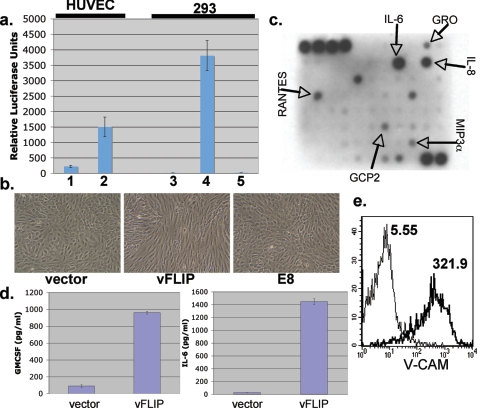
FIG. 3.
NF-κB activation correlates with spindle cell formation and upregulates inflammatory cytokines and markers of endothelial activation. (a) Bars 1 and 2, Spindled vFLIP-expressing HUVECs (1) and HUVECs expressing vector alone (2) were transfected with 0.5 μg NF-κB-luciferase reporter construct and 0.5 μg β-galactosidase-encoding plasmid to normalize for transfection efficiency. Forty-eight hours posttransfection, luciferase and β-galactosidase assays were performed; bars show normalized levels of luciferase activity. Bars 3, 4, and 5, 293 cells were transfected with equal amounts of vector (3), vFLIP (4), or E8 (5) plasmids along with an NF-κB-luciferase reporter and β-galactosidase construct. Error bars indicate standard deviations. Assays were performed at 48 h posttransfection. (b) HUVECs were transduced with retrovirus encoding either vFLIP, E8, or empty vector and selected with puromycin as described before. Images were taken 3 days posttransduction. (c) Supernatant conditioned for 24 h by fully spindled HUVECs expressing vFLIP was applied to the RayBio human cytokine antibody array V as per the manufacturer's indications. The cytokines indicated by arrows are those found to be increased over conditioned medium from vector-expressing HUVECs assayed in parallel. (d) Medium from vFLIP or empty vector-expressing HUVECs was assayed for content of IL-6 or granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) by ELISA. Error bars indicate standard deviations. (e) Spindle cells expressing vFLIP (thick line) or vector-transduced HUVECs (thin line) were stained for surface expression of VCAM-1 and examined by flow cytometry. Numbers next to histograms indicate geographic means of expression levels.