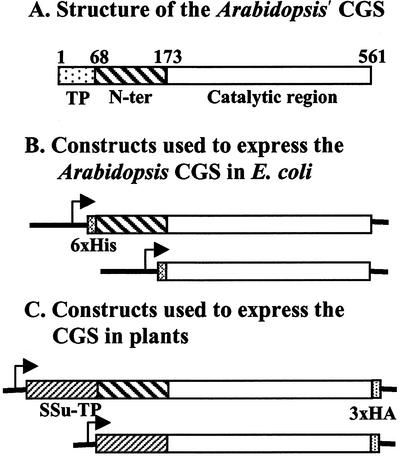
Figure 1.
A, Schematic presentation of Arabidopsis CGS protein. The amino acids are numbered from the first Met of the protein in the transit peptide. TP, the chloroplast-targeting transit peptide, which directs the protein into the chloroplast and is then removed. N-ter, the N-terminal region of CGS (following removal of the transit peptide), which shares no homology to CGSs of bacteria. Catalytic region, the part of CGS sharing a high homology to bacteria CGSs and harboring the catalytic site. B, The constructs used to express the full-length or truncated Arabidopsis CGS in bacteria. A six-His tag was added at the N terminus to the constructs of the bacteria expressed proteins. C, The constructs used to express the full-length or truncated Arabidopsis CGS in plants. The transit peptide of the Rubisco small subunit 3A of pea (Ssu-TP) was used instead of the endogenous one. The sequence encoding three hemagglutinins (3xHA) was added in frame at the C terminus of the protein. Transcription promoters are symbolized by arrows.