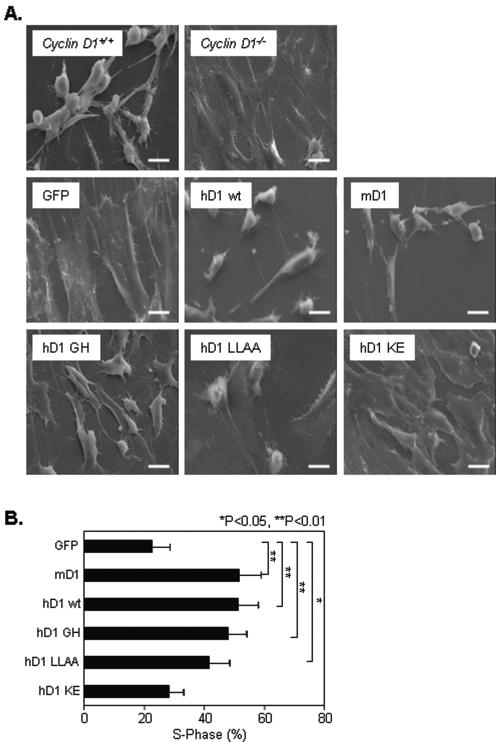
FIG. 3.
The cdk-binding domain of cyclin D1 regulates cellular spreading. (A) cyclin D1+/+, cyclin D1−/−, and cyclin D1−/− MEFs infected with either MSCV-GFP vector or wild-type or mutant mouse (mD1) or human (hD1) cyclin D1 were plated on fibronectin (10 μg/ml)-coated coverslips and examined by scanning electron microscopy (×1,000). Scale bar, 20 μm. (B) DNA synthesis and cell cycle analysis of MEFs were performed by propidium iodide staining and FACS analysis. Cells were either infected with MSCV-GFP vector control or viruses encoding murine or human cyclin D1 wild type (wt) or mutants, as indicated. * and ** indicate significant difference between wild-type or mutant cyclin D1-infected cells and MSCV-GFP control cells.