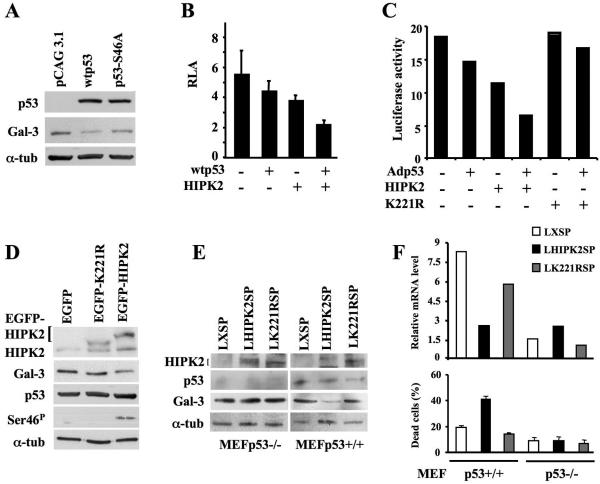
FIG. 3.
p53 phosphorylation at Ser46 by HIPK2 is required for p53-mediated repression of Gal-3. (A) Immunoblots with antibodies to p53 and Gal-3 on H1299 cells transfected with pCAG3.1 control, pCAG3.1-wtp53, or pCAG3.1-p53S46A mutant vector. α-Tubulin was used as a loading control. (B) Coexpression studies were performed in human H1299 cells by transfecting the p(−836/+141)LGALS3-Luc reporter vector with wtp53 and/or HIPK2 expression vectors. Means ± standard deviations of at least seven independent experiments are reported. (C) Luciferase activity of the same p(−836/+141)LGALS3-Luc reporter vector stably transfected into H1299 cells. The polyclonal population was infected with Adp53 at MOI of 10 and transiently transfected with HIPK2- or K221R mutant-expressing vectors. The results of one indicative experiment out of three performed are reported. (D) Immunoblot of total p53 and p53 phosphorylation at Ser46 (Ser-46P), HIPK2, and Gal-3 in p53-positive HEK293 cells transiently transfected with pEGFP vectors encoding EGFP-tagged wild-type HIPK2 or its KD K221R mutant. α-Tubulin was used as a loading control. (E and F) MEFs from p53+/+ and p53−/− mice were infected with recombinant LHIPK2SP, LK221RSP, or control LXSP retroviruses. At 36 h postinfection, cells were harvested to perform Western blotting on the indicated proteins (E) and real-time RT-PCR on the gal-3 transcript (F, upper panel) and to measure cell death (F, lower panel). α-tub, α-tubulin.