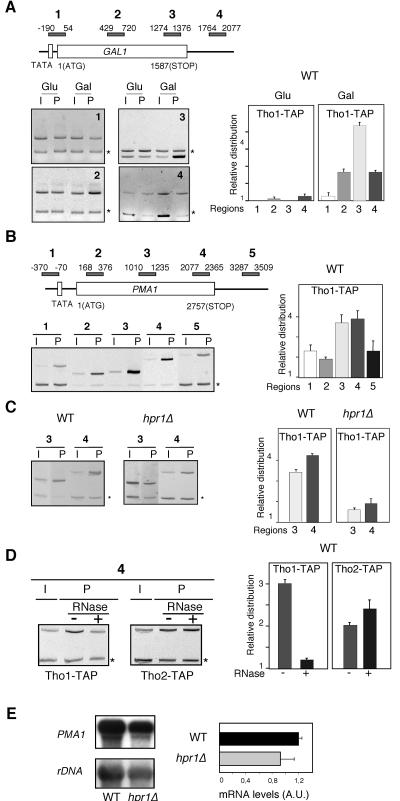
FIG. 4.
Tho1 binds to actively transcribed chromatin in a THO- and RNA-dependent manner. The scheme of the genes analyzed and the PCR fragments amplified by PCR are shown. One representative acrylamide electrophoresis for each experiment is shown, with the PCR fragment corresponding to the bp 9716 to 9863 intergenic region of chromosome V used as a control indicated with asterisks. (A) ChIP analysis of Tho1 at the endogenous GAL1 gene in the wild-type strain WWT1T. (B) ChIP analysis of Tho1 at the endogenous PMA1 gene in the wild-type (WT) WWT1T strains carrying the TAP-tagged Tho1. (C) Importance of the THO complex for the recruitment of Tho1 to chromatin at the PMA1 gene, as determined by comparative ChIP analysis in the wild type (WWT1T) and hpr1Δ mutant (WHT1T) (D) Effect of RNase treatment on Tho1 and Tho2 recruitment to active chromatin at the PMA1 gene, as determined by modified ChIP analyses. These were performed in the wild-type WWT1T and WWT2T strains, carrying TAP-tagged Tho1 and Tho2, respectively, treated with (+) or without (−) RNase before immunoprecipitation. Cross-linking times were reduced to 4 min in either treated or nontreated samples. (E) Northern analyses of the expression of PMA1 in WT and hpr1Δ congenic strains RNA was isolated from mid-log-phase cultures grown in rich media. As a 32P-labeled DNA probe, we used the 2.7-kb PMA1 fragment and an internal 589-bp 25S rRNA fragment, both obtained by PCR. Other details are as described for Fig. 1 and 2. AU, arbitrary units. Error bars indicate standard deviations.