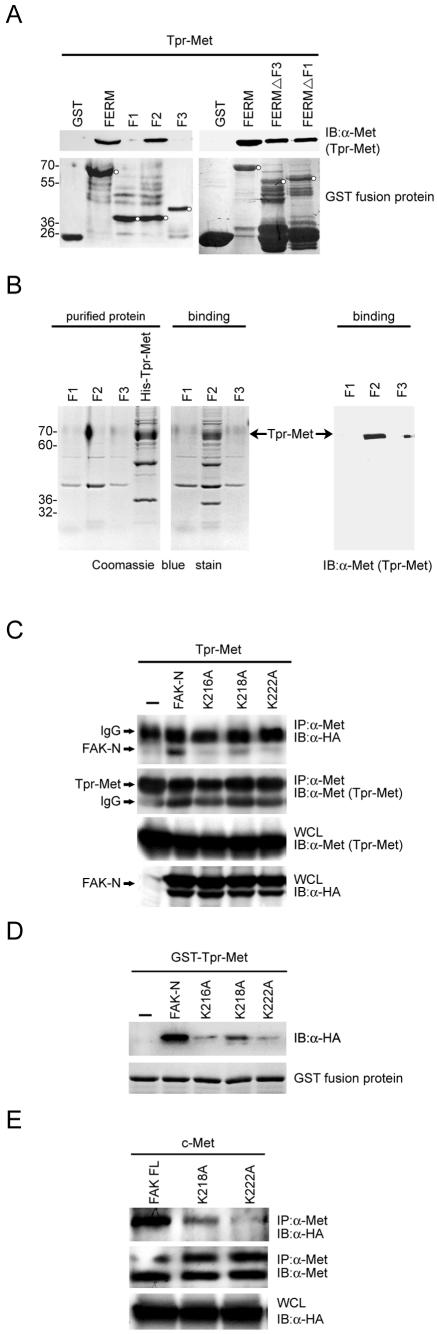
FIG. 5.
The basic residues in the F2 subdomain of the FAK FERM domain are critical for FAK to interact with Met. (A) Immobilized GST fusion proteins encoding the FAK FERM domain or its truncated mutants were incubated with HEK 293 cell lysates containing Tpr-Met. The bound proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting (IB) with anti-Met (α-Met). The GST fusion proteins on the nitrocellulose membrane were visualized by staining with Ponceau S solution. The intact GST fusion proteins on the membrane are marked by circles. (B) Immobilized GST fusion proteins encoding the F1, F2, or F3 subdomain of the FAK FERM domain were incubated with purified histidine-tagged Tpr-Met (His-Tpr-Met). The bound proteins were resolved by SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and visualized by Coomassie blue staining (left) or subjected to immunoblotting with anti-Met (right). (C) Tpr-Met was transiently coexpressed with the HA-tagged FAK NH2 domain or its mutants in HEK 293 cells. Coprecipitation of Tpr-Met and the HA-tagged FAK NH2 domain was analyzed. (D) Immobilized GST-Tpr-Met was incubated with HEK 293 cell lysates containing the HA-tagged FAK NH2 domain or its mutants. The bound proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-HA. (E) c-Met was transiently coexpressed with HA-tagged full-length (FL) FAK or its mutants in HEK 293 cells. Coprecipitation of c-Met with HA-tagged FAK was analyzed. Molecular size markers (in kilodaltons) are noted at the left of blots. IgG, immunoglobulin G; IP, immunoprecipitation; WCL, whole-cell lysates.