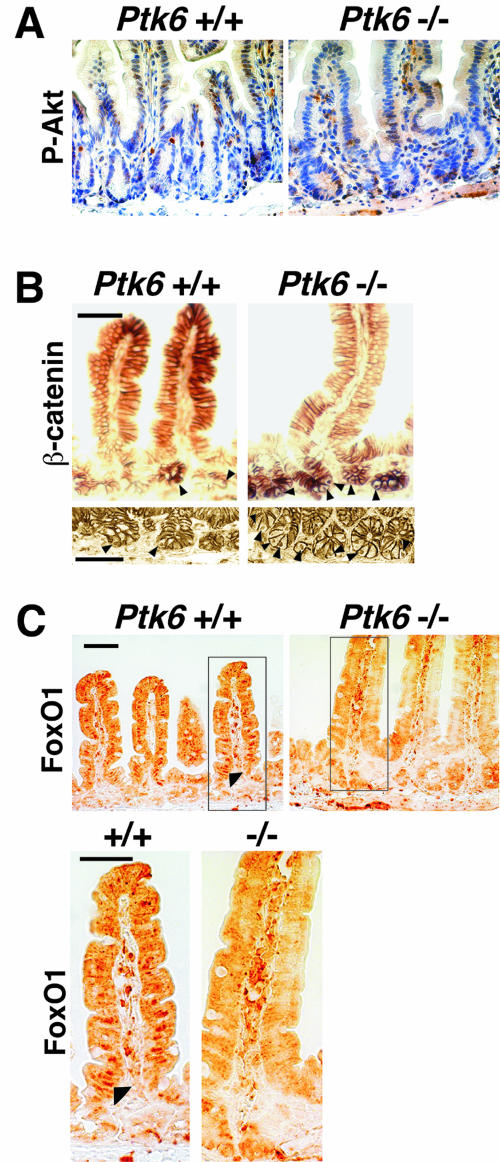
FIG. 8.
Increased Akt activation and nuclear β-catenin, and altered FoxO1 localization, the in Ptk6−/− intestine. A. Increased phospho-Akt(Ser473) immunoreactivity is evident in crypts and villi of the Ptk6−/− small intestine. Antibody binding was detected with DAB (brown), and sections were counterstained with hematoxylin. B. Increased numbers of β-catenin-positive nuclei were detected in crypts of PTK6-deficient mice. β-Catenin is localized at the membrane in the crypt and villus epithelial cells and in nuclei of crypt epithelial cells (arrowheads). C. Decreased nuclear localization of the Akt substrate FoxO1 is detected in Ptk6−/− intestine. The boxed region is magnified, and altered and the arrowhead shows nuclear FoxO1 in the wild-type epithelium. This supports our observation that Akt activity is increased in Ptk6−/− intestine because Akt negatively regulates its FoxO protein substrates by promoting nuclear exclusion of these transcription factors. FoxO1 antibody binding was detected with DAB (brown). No counterstain was used. Bars, 50 μm.