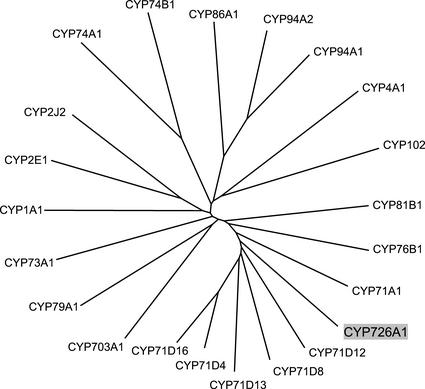
Figure 3.
Phylogenetic comparison of the E. lagascae CYP726A1 with selected members of the cytochrome P450 superfamily. The unrooted phylogenetic tree shown was generated by use of the neighbor-joining algorithm (Saitou and Nei, 1987). The P450s represented (and corresponding GenBank accession numbers) are as follows: CYP1A1, human (Homo sapiens) arachidonic acid epoxygenase (K03191); CYP2E1, Mus musculus lauric acid ω-1 hydroxylase (X62595); CYP2J2, human arachidonic acid epoxygenase (U37143); CYP94A2, common vetch (Vicia sativa) medium chain fatty acid hydroxylase (AF092917); CYP94A1, common vetch fatty acid ω-hydroxylase (AF030260); CYP86A1, Arabidopsis fatty acid ω-hydroxylase (X90458); CYP4A1, Rattus norvegicus fatty acid ω-hydroxylase (M57718); CYP74B1, Capsicum annuum fatty acid hydroperoxide lyase (U51674); CYP74A1, flax (Linum usitatissimum) allene oxide synthase (U00428); CYP102, Bacillus megaterium fatty acid in-chain hydroxylase (J04832); CYP73A1, Jerusalem artichoke (Helianthus tuberosus) cinnamate 4-hydroxylase (Z17369); CYP79A1, Sorghum bicolor Tyr N-hydroxylase (U32624); CYP703A1, Petunia × hybrida lauric acid monooxygenase (AB006790); CYP76B1, Jerusalem artichoke 7-ethoxycoumarin O-deethylase (Y09920); CYP81B1, Jerusalem artichoke fatty acid in-chain hydroxylase (AJ000477); CYP71A1, avocado (Persea americana) monoterpene monooxygenase (M32885); CYP71D8, soybean elicitor-induced P450 (unknown function) (O81974); CYP71D13, Mentha sp. (-)-(4S)-limonene-3-hydroxylase (AF124816); CYP71D4, potato fungus-induced P450 (unknown function) (AJ296346); and CYP71D12, Catharanthus roseus tabersonine 16-hydroxylase (AJ238612); and CYP71D16, tobacco cembratriene-ol hydroxylase (AF166332). The E. lagascae CYP726A1 (AF406732) is highlighted in gray.