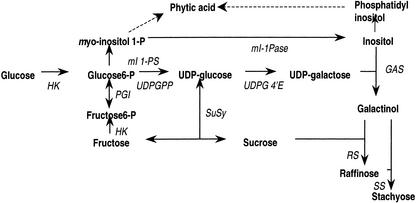
Figure 1.
A schematic diagram of the interactions involved inconversion of carbon from Glc into either phytic acid or Suc, raffinose, and stachyose. HK, Hexokinase; PGI, phospho-Glc iosmerase; UDPGP, uridine diphospho-Glc phyrophosphorylase; UDPG 4′E, uridine diphospho-Glc 4′ epimerase; SuSy, Suc synthase; GAS, galactinol synthase; RS, raffinose synthase; SS, stachyose synthase; mI-1pase, myo-inositol 1-phosphate phosphatase; mI 1PS, myo-inositol 1-phosphate synthase. The product of the reaction catalyzed by myo-inositol 1-phosphate synthase (EC 5.5.1.4) is l-myo-inositol 1-phosphate in the l-convention nomenclature or d-myo-inositol 3-phosphate in the d-convention nomenclature. The naming of genes that catalyze this reaction has followed the l-convention nomenclature. Because the soybean genes described in this paper were cloned by homology to already named genes, the l-convention nomenclature is maintained here and extends to the reaction products.