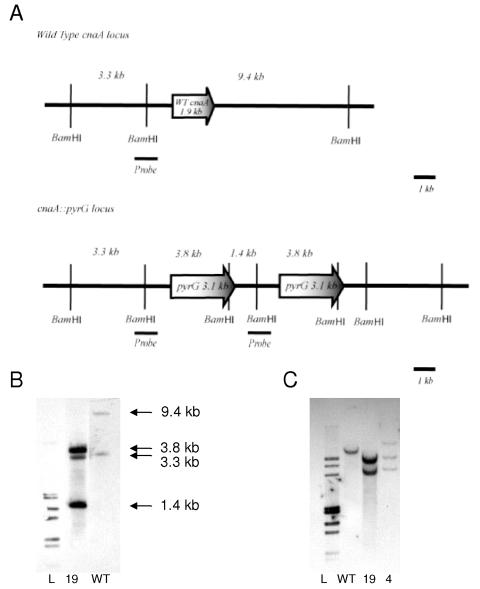
FIG. 1.
Construction of ΔcnaA mutant and complement of A. fumigatus. (A) In the ΔcnaA mutant, wild-type A. fumigatus cnaA (1.9 kb) is replaced by the 3.1-kb A. parasiticus pyrG gene. The ΔcnaA mutant was created by tandem insertional replacement of the pyrG in the cnaA locus. The short, dark bar is the 1.1-kb probe of the upstream flanking sequence used for Southern analyses. (B) Southern analyses were performed on BamHI-digested genomic DNA which was probed with the 1.1-kb probe of the upstream flanking sequence to demonstrate a tandem insertion and replacement of cnaA. Additional Southern analyses with HindIII-, KpnI-, ApaI-, and NdeI-digested genomic DNA and probing with both the upstream flanking sequence and a pyrG probe (data not shown) confirmed the tandem insertion. (C) Complementation of the ΔcnaA mutant was confirmed by AgeI-digested genomic DNA probed with the same 1.1-kb probe to reveal both the cnaA::pyrG deletion allele and a single ectopic copy of the wild-type cnaA gene (ΔcnaA + cnaA strain). L, ladder; WT, wild type; 19, ΔcnaA mutant; 4, ΔcnaA + cnaA strain.