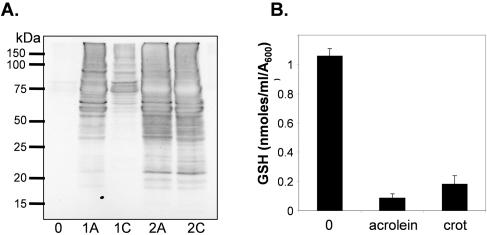
FIG. 5.
Acrolein and crotonaldehyde cause similar levels of cellular damage. (A) Protein carbonylation is induced by exposure to acrolein and crotonaldehyde. Wild-type cells were grown in minimal media to exponential phase (A600 = 0.6) and treated with 1 mM or 2 mM acrolein (A) or crotonaldehyde (C) for 1 h. Protein extracts were treated with the carbonyl-specific probe, DNPH, and analyzed by Western blot analysis using an antibody against DNPH. (B) Acrolein and crotonaldehyde (crot) deplete cellular glutathione. Wild-type cells were grown in minimal media to exponential phase (A600 = 0.6) and treated with 0.2 mM acrolein or 0.5 mM crotonaldehyde for 1 h. The GSH concentrations shown are the means for three determinations and are given as nmol/ml/A600.