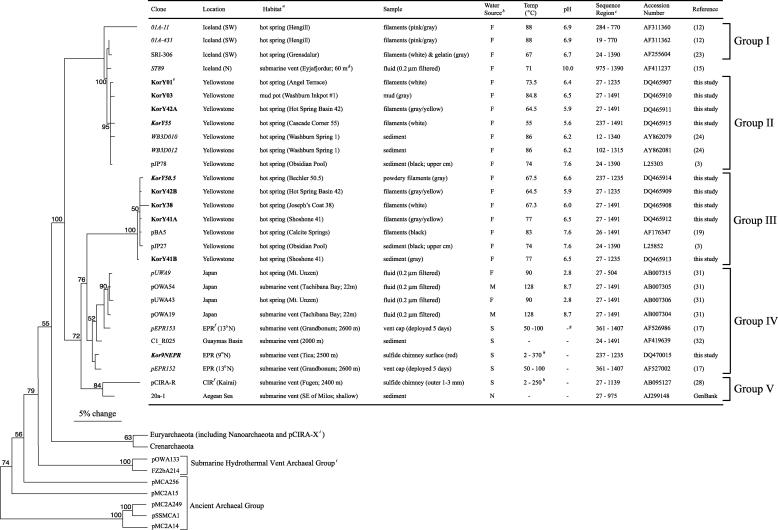
FIG. 1.
Phylogram of Korarchaeota based on 16S rRNA gene sequences. The samples, sites, and chemical and physical characteristics of the environments from which they were PCR amplified, length of the sequences, accession numbers, and references are also listed. Major phylogenetic groupings are bracketed on the right. The tree topology and bootstrap values were generated by parsimony analysis of the 946-nt alignment. Partial sequences were added by using the ARB parsimony tool (italicized clone names) and thus have no bootstrap values. The sequences identified in the present study are shown in boldface. Escherichia coli, Homo sapiens, and 46 diverse Archaea small subunit rRNA genes were used as outgroups (shown with branches shortened and Euryarchaeota and Crenarchaeota branches collapsed). The scale bar = 5% change in nucleotide sequence. Superscript letters: a, hot springs and mudpots are terrestrial; b, F = freshwater, S = seawater, M = mix, N = not reported; c, numbering is based on E. coli; d, depth below seawater surface (where not noted = surface); e, the Korarchaeota clone naming terminology is “Kor” + Y (Yellowstone) + inventory sample number; f, EPR = East Pacific Rise, CIR = Central Indian Ridge; g, a dash means not reported; h, sulfide chimney separated cold ambient seawater and hot hydrothermal fluid; i, previously referred to as Korarchaeota.