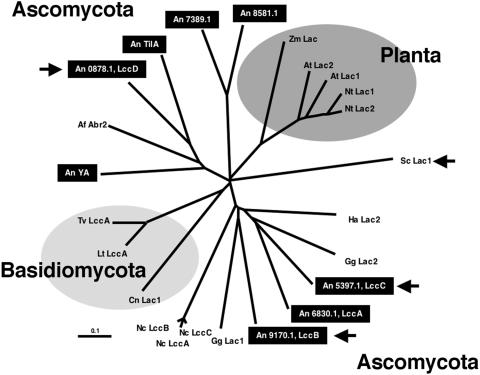
FIG. 5.
Phylogenetic tree of different plant and fungal laccases and ascorbate oxidases. The tree was generated with the ClustalW algorithm from the ClustalX 1.8 program with standard parameters. The gene names and accession numbers are indicated as follows: A. fumigatus, Af Abr2 (AF104823); A. nidulans, An TilA (AJ305224), An YA (X52552), An0878.1, An5397.1, An6830.1, An7389.1, An8581.1, An9170.1; Arabidopsis thaliana, At Lac1 (NP_565881), At Lac2 (NP_195739); Cryptococcus neoformans, Cn Lac1 (A36962); Gaeumannomyces graminis var. graminis, Gg Lac1 (AJ437319), Gg Lac2 (AJ437320); Hortaea acidophila, Ha Lac1 (AAY33971); Lentinus tigrinus, Lt Lac1 (AAX07469); Neurospora crassa, Nc LccA (AAA33591), Nc LccB (AAA33592), Nc LccC (AAA33590); Nicotiana tabacum, Nt Lac1 (AAC49538), Nt Lac2 (AAC49536); Trametes versicolor, Tv LacA (A35883); Zea mays, Zm Lac1 (AAX83113); S. chartarum, Sc Lac1 (AAY23005). The dendrogram was visualized by TreeView. The scale is about 10% calculated sequence divergence. The arrows indicate the four laccases studied in this paper.