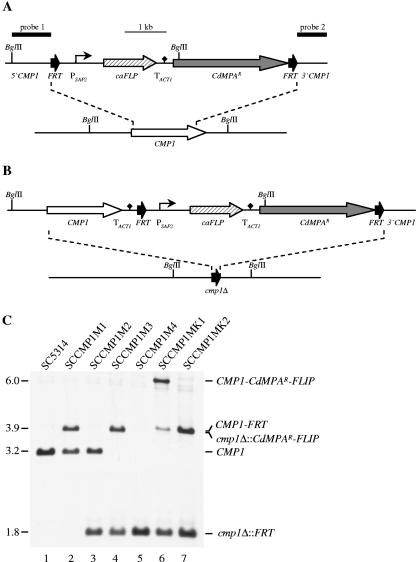
FIG. 1.
Construction of the C. albicans cmp1 deletion mutant and complemented strain. (A) Structure of the CMP1 deletion cassette (top) and genomic structure of the CMP1 locus in the parent strain SC5314 (bottom). The CMP1 coding region is represented by the white arrow, and the upstream and downstream sequences by the solid lines. The direct repeats of the 34-bp FRT site (black arrows) bordering the CdMPAR flipper cassette are not drawn to scale. The SAP2 promoter (PSAP2) is indicated by the bent arrow, the caFLP gene by the hatched arrow, the transcription termination sequence of the ACT1 gene (TACT1) by the black diamond, and the CdMPAR marker by the gray arrow. The diagnostic BglII sites are shown, and the DNA fragments used for Southern hybridization analysis of the mutants are indicated by thick bars (probe 1 and probe 2). (B) Structure of the DNA cassette (top) which was used for reintegration of an intact CMP1 copy (white arrow) into one of the inactivated cmp1Δ alleles (bottom). (C) Southern hybridization of BglII-digested genomic DNA of the parent strain SC5314 and mutant derivatives with the CMP1-specific probe 1. The sizes of the hybridizing fragments (in kilobases) are given on the left of the blot, and their identities are indicated on the right.