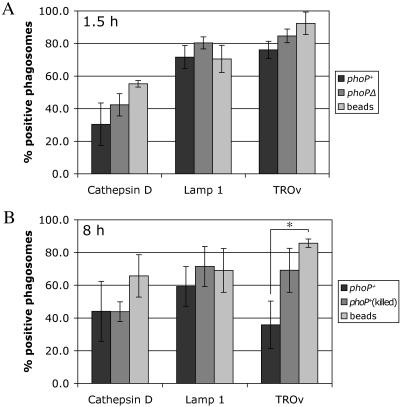
FIG. 4.
Percentages of Y. pestis- and bead-containing phagosomes associated with a lysosomal marker. (A) J774A.1 macrophages were infected with GFP-expressing Y. pestis strain KIM5/GFP or KIM5phoPΔ/GFP (MOI, 10) or incubated with latex beads. After 1.5 h of incubation, the macrophages were fixed and processed as described in the legend to Fig. 3 to detect colocalization of phagosomes with Lamp1, cathepsin D, or TROv by confocal microscopy. For the TROv experiments, macrophages were allowed to pinocytose the label for 30 min and then incubated in the absence of TROv for 2.5 h prior to incubation with bacteria or beads. (B) J774A.1 macrophages were infected with GFP-expressing live or gentamicin-killed Y. pestis KIM5/GFP or incubated with latex beads. After 8 h of incubation, the macrophages were fixed and processed as described above for confocal microscopy. For the TROv experiments, the label was added 5 h after exposure to bacteria or beads for 30 min. Incubation was then continued in the absence of TROv for 2.5 h to allow the label to accumulate in lysosomes. For each experiment and each marker 50 phagosomes were analyzed by confocal microscopy to determine the colocalization of the GFP signal with the lysosomal marker. The data are the averages of three independent experiments. The error bars indicate standard deviations. The asterisk indicates that the difference is statistically significant.