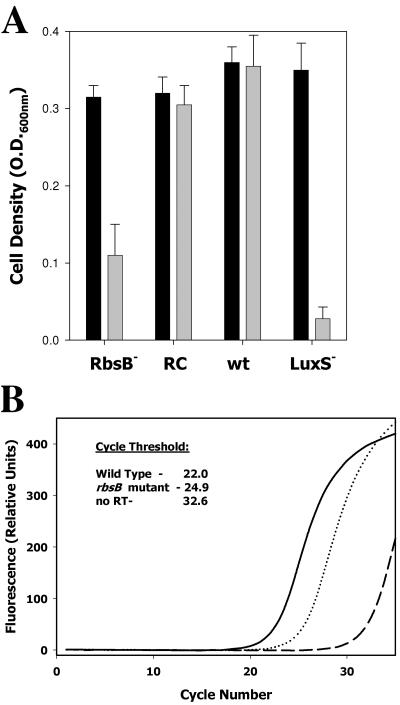
FIG. 6.
Inactivation of A. actinomycetemcomitans rbsB influences aerobic growth under iron limitation and expression of afuA, encoding a ferric iron transporter. (A) Levels of growth of wild-type A. actinomycetemcomitans (wt), isogenic rbsB and luxS mutants (RbsB− and LuxS−, respectively), and the rbsB mutant complemented with a plasmid-borne copy of rbsB (RC) were determined under iron-replete conditions (black bars) and in the presence of 100 μM EDDHA (gray bars). Cultures were analyzed at mid-exponential to late exponential phases of growth by determining optical density at 600 nm (O.D.600nm). The results presented are averages from three independent experiments. (B) Expression of afuA was monitored by real-time PCR using gene-specific primers and the fluorophore SYBR green. Fluorescence as a function of cycle number was plotted for reactions using RNA from wild-type A. actinomycetemcomitans (solid line) and an isogenic rbsB mutant (dotted line). Results from a negative-control reaction using RNA from the mutant strain but without reverse transcriptase (RT) are shown by the dashed line. The cycle threshold was calculated from the raw fluorescence data by using the onboard analysis software supplied with the SmartCycler system.