Fig. 4.
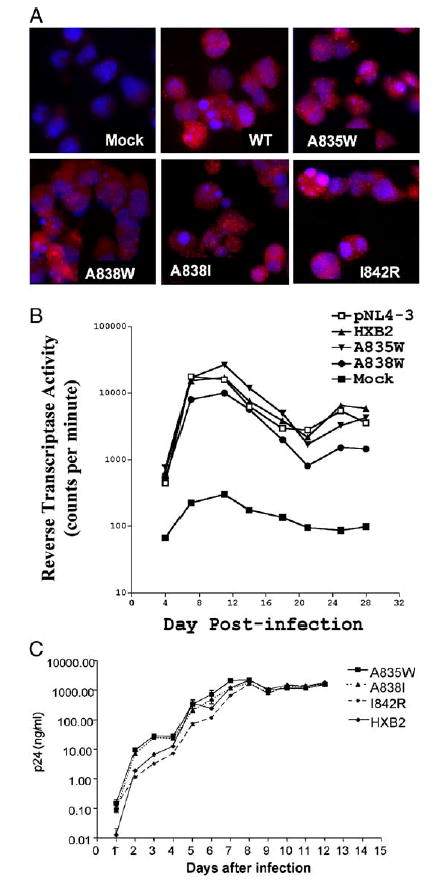
Effect of gp41 point mutations on HIV production in H9 cells infected with HIV-1. (A) H9 cells were infected with HIV-1 NL4.3, NL4.3 with the BamHI/XhoI fragment of wild type HXB2 env (HXB2) inserted, or NL4.3 containing the gp41 mutations A835W, A838W, A838I, or I842R. On day 10 post-infection, cells were collected and stained for gp120 by immunohistochemistry (red), and with Hoechst dye to identify nuclei (blue). Shown is a representative photomicrograph of three independent experiments. Identical results were obtained in separate infections on day 7 post-infection (data not shown). (B) H9 cells were infected as in panel A and at three day intervals beginning on day 4 following infection, culture supernatants were collected and assayed for reverse transcriptase (RT) activity. The mean RT activities of triplicate samples are shown. (C) H9 cells were infected as in panel A with env point mutants A835W, A838I, and I842R. Cell culture supernatants were collected at daily intervals following infection and viral p24 levels were determined in triplicate by ELISA. Points represent averages of three independent infections, ± SEM.
