Fig. 5.
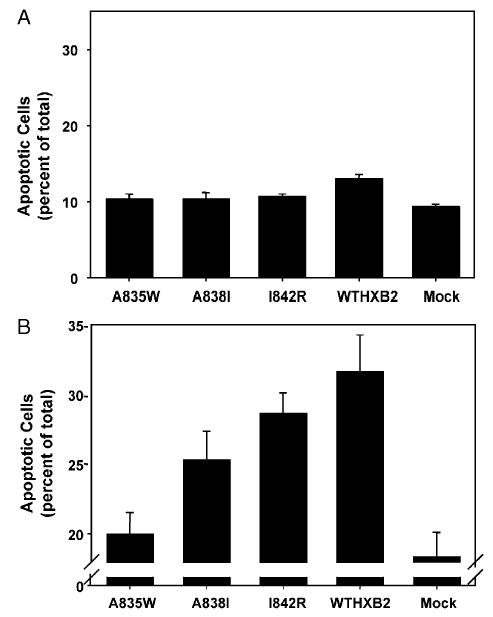
(A) Spontaneous apoptosis in H9 cells infected with HIV-1. H9 cells were infected with HIV-1 NL4.3 with the BamHI/XhoI fragment of the wild-type HXB2 env gene (WTHXB2) inserted or the same viral construct containing the indicated point mutations in gp41. Spontaneous apoptosis was determined on day 5 post-infection by Hoechst staining and morphological analysis of nuclei. Shown are the results of three independent infections, indicating mean percentage of apoptotic cells ±SEM. (B) Fas-mediated apoptosis in H9 cells infected with HIV-1. H9 cells were infected with HIV-1 NL4.3 with the BamHI/XhoI fragment of the wild-type HXB2 env gene (WTHXB2) inserted or the same viral construct containing the indicated point mutations in gp41. Cells were treated with 500 ng/ml anti-fas on day 5 post-infection for 1 h followed by fixation and Hoechst staining and morphological analysis of nuclei. Fas-mediated apoptosis was calculated by subtracting the value for spontaneous apoptosis from the value for apoptosis following fas antibody treatment. Data represent the mean percentage of apoptotic cells from three independent experiments, ±SEM.
