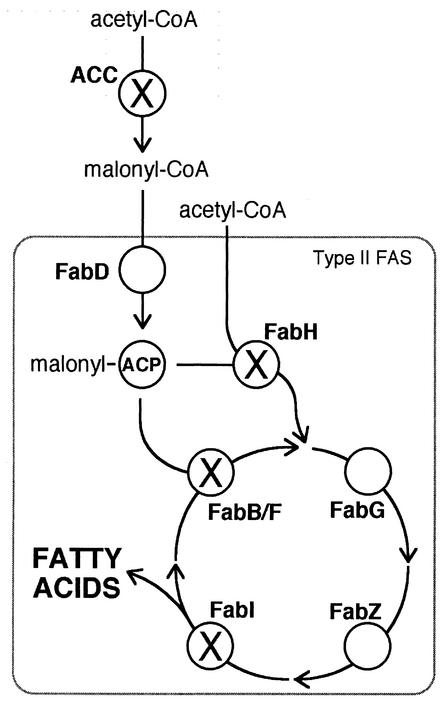
FIG. 1.
Pathway of type II de novo fatty acid biosynthesis showing key enzymes (boldface) and substrates. Enzymes belonging to the FAS complex are indicated by the box. The substrate for FAS, malonyl-CoA, is formed from acetyl-CoA by ACC. Fatty acid elongation consists of rounds of priming ACP with a malonyl moiety followed by condensation, reduction, dehydration, and reduction reactions that add two carbons to the growing acyl chain in each round. The first condensation reaction is catalyzed by FabH, and subsequent condensation reactions are catalyzed by FabB and/or FabF. Enzymes marked with an “X” are targets for inhibitory drugs that are the subjects of this investigation. FabD, malonyl-CoA:ACP transacylase; FabB, FabF, and FabH, β-ketoacyl-ACP synthases I, II, and III, respectively; FabG, β-ketoacyl-ACP reductase; FabZ, β-hydroxyacyl-ACP dehydratase; FabI, enoyl-ACP reductase.