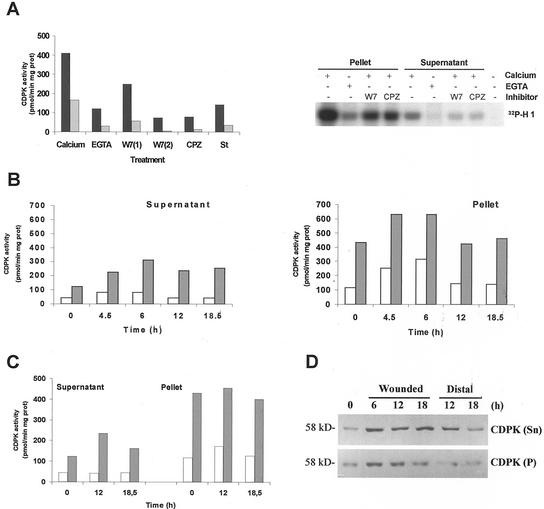
Figure 7.
A, CDPK activity was determined in soluble (gray bars) and particulate (black bars) fractions. A standard assay was performed using syntide-2 as substrate in the presence of 1 mm EGTA or 1 mm CaCl2. CPZ (0.5 mm), 0.25 (1) or 1 mm (2) W7, and 1 μm staurosporine (St) were tested in the presence of 1 mm CaCl2. Alternatively, extracts were incubated with 0.1 mg mL−1 histone H1 and 10 μm [γ-32P]ATP in the presence of 1 mm EGTA or 1 mm CaCl2. The same reaction was carried out in the presence of CPZ, W7, or staurosporine. Phosphorylated samples were analyzed on 12% (w/v) SDS-PAGE. Specific CDPK activity was expressed as picomoles of 32P incorporated per minute per milligram of protein. Time course induction of CDPK activity in response to wounding. Soluble (Supernatant) and particulate (Pellet) fractions were obtained from control and wounded leaflets (B) or distal leaves (C) at the times indicated in the figure. CDPK activity was assayed using syntide-2 as substrate in the presence of 1 mm EGTA (white bars) or 1 mm CaCl2 (gray bars). Specific CDPK activity was expressed as above. D, Western-blot analysis of soluble (50 μg) and particulate (100 μg) protein extracts from control, wounded, or distal leaves. Membranes were incubated with a polyclonal antibody (1:4,000) against the CLD domain of soybean CDPK.