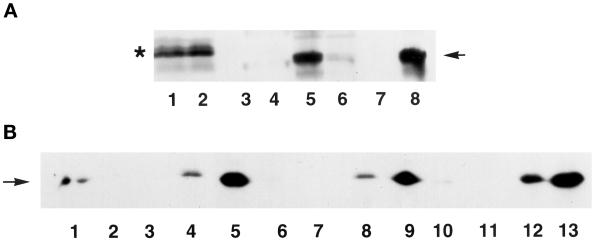
Figure 12.
Western blot analysis of HA-tagged Hic-5 and its fragments in subcellular fractions of Cos-1 cells. (A) Cos-1 cells were transfected with an expression vector for either the N-terminal (amino acids 1–200; lanes 1–4) or C-terminal (amino acids 201–444; lanes 5–8) fragment of HA-tagged Hic-5. Proteins present in whole cell extracts (lanes 1 and 5), CK buffer–extracted supernatants (lanes 2 and 6), DNAse I–digested supernatants (lanes 3 and 7), or nuclear matrix pellets (lanes 4 and 8) were separated by SDS-PAGE and subjected to Western blot analysis to detect HA-tagged Hic-5. The asterisk indicates the position of the N-terminal Hic-5 fragment, and the arrow points to the C-terminal Hic-5 fragment. The N-terminal fragment of Hic-5 migrates anomalously slower than the larger C-terminal fragment. (B) Samples from Figure 11 and Figure 12A were also probed on a separate blot to detect lamin B protein. Lanes 1–4 contain fractions from cells expressing full-length Hic-5 (from Figure 11, lanes 1–4); lanes 5–8 contain fractions expressing the N-terminal Hic-5 fragment (from panel A, lanes 1–4); and lanes 9–12 contain fractions expressing the C-terminal Hic-5 fragment (from panel A, lanes 5–8). Lane 13 contains whole cell extract from untransfected cells.