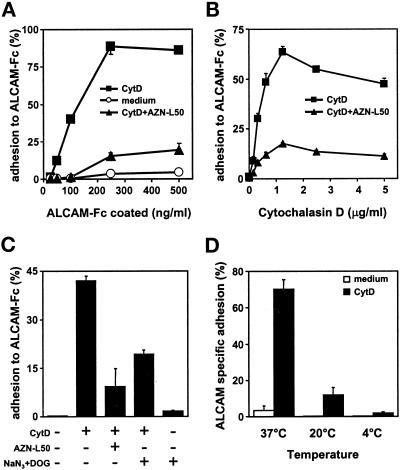
Figure 2.
(A) CytD-induced adhesion is dependent on the concentration of ALCAM-Fc. Untreated (open circles) or CytD-pretreated (2.5 μg/ml, 30 min at 37°C; open squares) K562-ALCAM cells were allowed to adhere for 45 min at 37°C to increasing amounts of ALCAM-Fc. Addition of the blocking antibody AZN-L50 (closed triangles) inhibits CytD-induced adhesion. Adhesion was quantified, and the mean percentage of cells bound to the plate ± SD is depicted. One experiment of three is shown. (B) Induction of ALCAM-mediated adhesion is dependent on the concentration of CytD. K562-ALCAM cells were preincubated with increasing concentrations of CytD, and adhesion to an ALCAM-Fc–coated plate (250 ng/ml) in the absence (closed squares) or presence (closed triangles) of the blocking mAb AZN-L50 was determined. The mean percentage of cells ± SD bound to the plate is expressed. One representative experiment of three is shown. (C) Cytochalasin D-induced ALCAM adhesion is energy dependent. K562-ALCAM cells were preincubated with CytD (2.5 μg/ml) in the presence or absence of a combination of deoxyglucose (DOG, 50 mM) and sodium azide (NaN3, 10 mM) to deprive the cells from energy or in the presence of the blocking mAb AZN-L50 (10 μg/ml). Control cells were preincubated with the combination of NaN3 and DOG without CytD. Subsequently, adhesion to immobilized ALCAM-Fc (250 ng/ml) for 45 min at 37°C was determined. Adhesion is expressed as the mean percentage of cells bound to the plate from triplicate wells ± SD. Data are representative of three experiments. (D) CytD-induced ALCAM-mediated adhesion is temperature dependent. K562-ALCAM cells were preincubated with CytD (2.5 μg/ml, 37°C; black bars) and subsequently allowed to adhere for 45 min at 37°C, RT, or at 4°C. Specific adhesion is expressed as the mean percentage ± SD of adherent cells from triplicate wells after subtraction of the adhesion in the presence of the blocking mAb AZN-L50. One experiment of three is shown.