Figure 2.
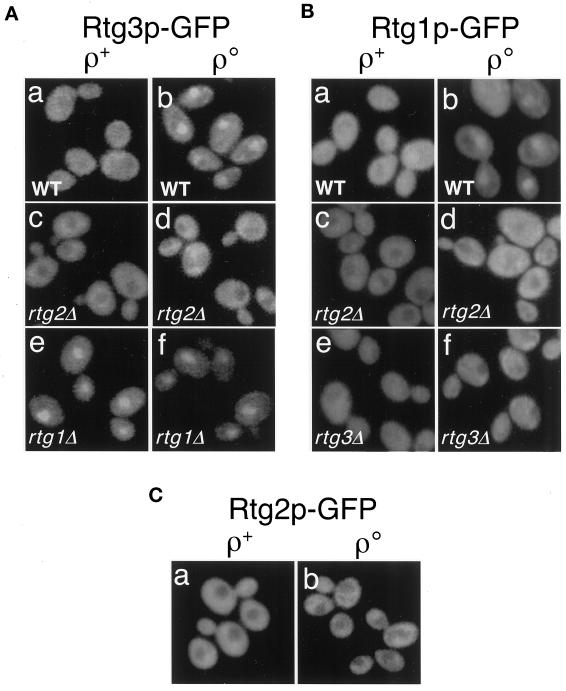
Subcellular localization of Rtg3p (A), Rtg1p (B), and Rtg2p (C) in wild-type (WT) and in various rtgΔ mutant derivatives of ρ+ and ρo cells. Constructs encoding C-terminal-tagged GFP derivatives of full-length Rtg1p, Rtg2p, and Rtg3p were transplaced into their respective chromosomal loci and expressed under the control of the each of the native promoters. Cells were grown in YNBR+cas medium. In wild-type ρ+ cells, Rtg3p-GFP (A, a) and Rtg1p-GFP (B, a) are largely cytoplasmic. In otherwise wild-type ρo cells, however, both Rtg3p-GFP (A, b) and Rtg1p-GFP (B, b) are concentrated in the nucleus. Rtg2p-GFP expressed from a single-copy gene transplaced into the RTG2 locus appears strictly cytoplasmic both in ρ+ and ρo cells (C, a and b). The effects of rtg1Δ, rtg2Δ, or rtg3Δ mutations on the subcellular localization of these GFP fusion proteins are shown. Localization of the GFP fusion proteins was determined by epifluorescence microscopy as described in MATERIALS AND METHODS.