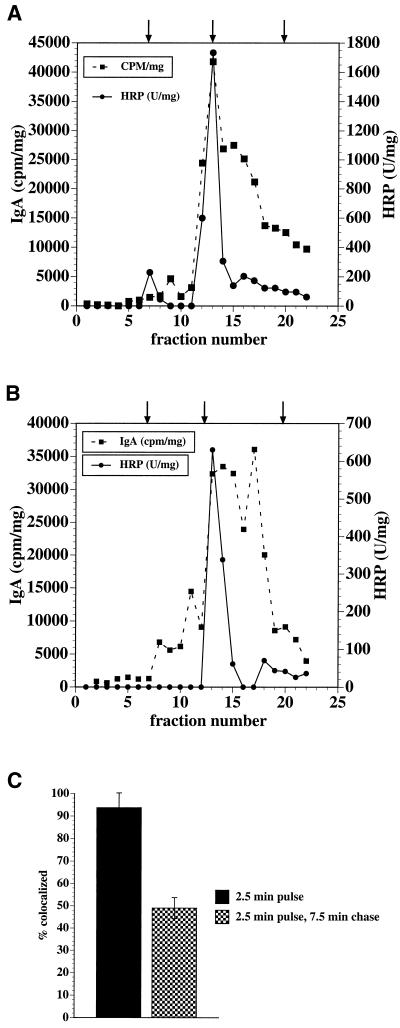
Figure 2.
Colocalization of fluid and membrane markers assessed by sucrose flotation gradients and by density-shift assays. (A and B) Sucrose flotation gradients. [125I]IgA and 5 mg/ml HRP were cointernalized for 2.5 min at 37°C from the apical poles of MDCK cells, and the cells were either rapidly chilled (A) or chased in marker-freemedium for 7.5 min at 37°C (B). The cells were homogenized, a postnuclear supernatant was generated, and the postnuclear supernatant (adjusted to 40.2% sucrose) was overlaid with 35, 25, and 8.5% (wt/wt) sucrose solutions. The samples were centrifuged, and 0.45-ml fractions were collected from the top of the gradient. Samples of each fraction were assayed for protein content, associated [125I]IgA (cpm), and HRP activity. The interfaces between the 40.2 and 35% sucrose layers, the 35 and 25% sucrose layers, and the 25 and 8.5% sucrose layers are indicated, from right to left, by arrows atop the panels. Data from a representative experiment are shown. (C) Density-shift assay. [125I]IgA and 5 mg/ml HRP were cointernalized for 2.5 min at 37°C from the apical poles of MDCK cells, and the cells were either rapidly chilled or chased in marker-free medium for 7.5 min at 37°C. Cell surface [125I]IgA was removed by trypsin treatment at 4°C. A DAB reaction was performed, cells were lysed in detergent, and the lysates were centrifuged. Details of the quantitation are given in MATERIALS AND METHODS. Results are mean ± SD (n ≥ 3).