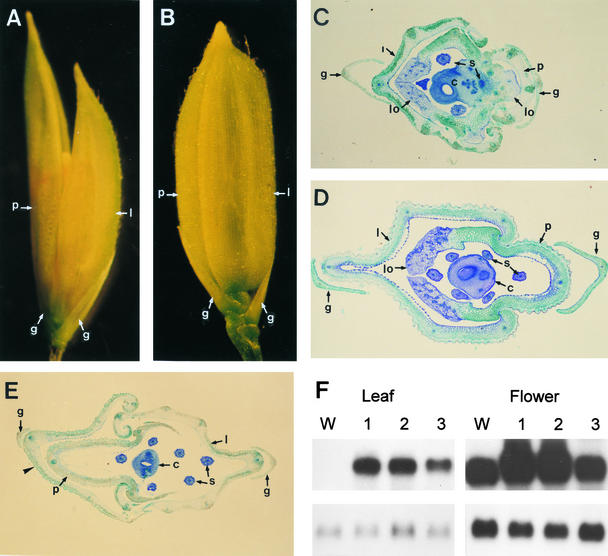
Figure 3.
Phenotypes of Transgenic Plants Expressing the OsAMDS1 Mutant.
(A) A spikelet from a plant of transgenic line 1703-1 transformed with pGA1703. The spikelet has a phenotype similar to lhs1, showing an open flower with the elongated leafy palea and lemma.
(B) A spikelet of a wild-type plant.
(C) A cross-sectioned spikelet from a plant of line 1703-1. The spikelet consists of normal glumes, abnormal palea and lemma, two pairs of leafy palea- and lemma-like lodicules, four stamens, and a carpel.
(D) A cross-sectioned wild-type spikelet. The spikelet has glumes, palea and lemma, a pair of lodicules, six stamens, and a carpel.
(E) A spikelet from the line 1703-3. The spikelet has an additional palea- and lemma-like structure (arrowhead). Original palea and lemma developed abnormally. Other organs—lodicules, stamens, and a carpel—are almost identical to the wild type.
(F) RNA gel blot analysis of the OsMADS1 transcript in the leaves and flowers of the 1703 transgenic lines. Five micrograms of total RNA from leaves (left) and 10 μg from flowers (right) were used for RNA gel blot analysis. At top, the amount of OsMADS1 transcript expressed was measured using the gene-specific probe for OsMADS1. Because of the similar sizes of the endogenous and transgenic OsMADS1 transcripts, the signals shown are the sum of the two. Lanes W, wild type; lanes 1, line 1703-1; lanes 2, line 1703-2; lanes 3, line 1703-3. At bottom are the controls. The same filters were washed and rehybridized with the rice α-tubulin gene OsTubA1 (Jeon et al., 2000).
c, carpel; g, normal glume; l, abnormal lemma; lo, leafy palea- and lemma-like lodicules; p, abnormal palea; s, stamen.