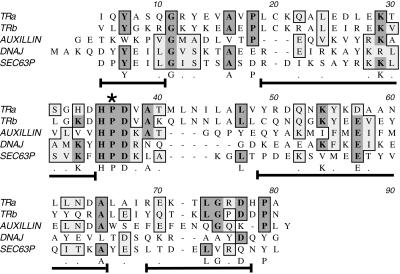
Figure 4.
Structure and sequence homologies between KLC tandem repeats and J-domains. Alignment of KLC tandem repeat sequences with a prokaryote J-domain sequence from Escherichia coli DnaJ and two eukaryotic J-domains from auxilin and Sec63P is shown (see DISCUSSION for more details). The invariant motifs are an essential HPD sequence (star) and the arrangement of short, flanking stretches of alpha helix (brackets under aligned sequences). The position of the alpha helical stretches is based on the nuclear magnetic resonance structure of the J-domains in DnaJ (Hill et al., 1995). Sequences in these helical stretches are more variable across family members, although some residues appear to be either conserved (letters under the sequence) or homologous (dots under sequence). Shading shows conserved residues in multiple J-domain sequences. This alignment shows that the primary sequences of tandem repeats 1–2 and 3–4 are consistent with a J-domain function.