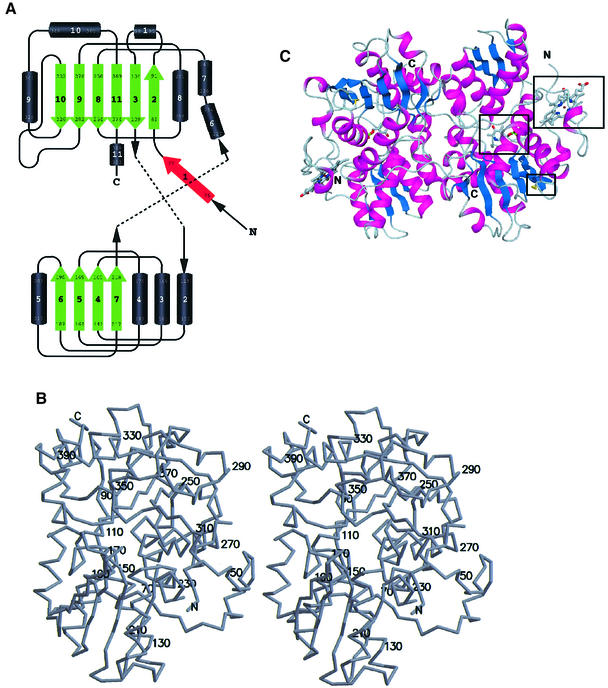
Fig. 2. Overall structure of truncated CBS. (A) Topology of the fold in CBS. Above, the C-terminal domain (with the first two strands of the β-sheet formed by the N-terminal residues); below, the N-terminal domain. Both domains are of the type α/β and contain a central β-sheet surrounded by several α-helices. Strand 1 (red) is part of the C-terminal β-sheet of the other monomer in the dimer. (B) Stereo drawing showing the overall fold of CBS with every twentieth residue labeled. (C) Schematic representation of the tertiary fold of a dimer of CBS. The central β-sheets are colored in blue and the surrounding α-helices are colored in magenta. In ball-and-stick representation and marked by a black box are the active site PLP, the heme and the oxidoreductase motif. The view is down the non-crystallographic 2-fold axis, which relates the two subunits of the dimer.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.